| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
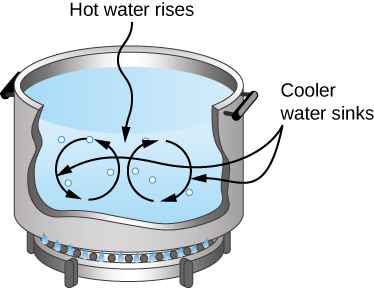
Natural convection like that of [link] and [link] , but acting on rock in Earth’s mantle, drives plate tectonics that are the motions that have shaped Earth’s surface.
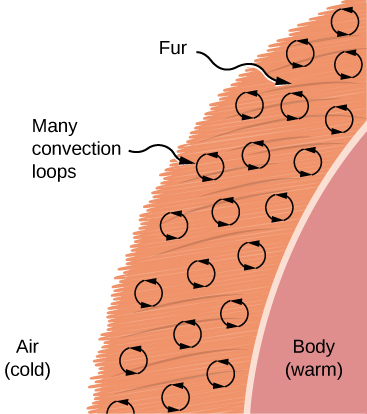
Convection is usually more complicated than conduction. Beyond noting that the convection rate is often approximately proportional to the temperature difference, we will not do any quantitative work comparable to the formula for conduction. However, we can describe convection qualitatively and relate convection rates to heat and time. However, air is a poor conductor. Therefore, convection dominates heat transfer by air, and the amount of available space for airflow determines whether air transfers heat rapidly or slowly. There is little heat transfer in a space filled with air with a small amount of other material that prevents flow. The space between the inside and outside walls of a typical American house, for example, is about 9 cm (3.5 in.)—large enough for convection to work effectively. The addition of wall insulation prevents airflow, so heat loss (or gain) is decreased. On the other hand, the gap between the two panes of a double-paned window is about 1 cm, which largely prevents convection and takes advantage of air’s low conductivity reduce heat loss. Fur, cloth, and fiberglass also take advantage of the low conductivity of air by trapping it in spaces too small to support convection ( [link] ).
Some interesting phenomena happen when convection is accompanied by a phase change. The combination allows us to cool off by sweating even if the temperature of the surrounding air exceeds body temperature. Heat from the skin is required for sweat to evaporate from the skin, but without air flow, the air becomes saturated and evaporation stops. Air flow caused by convection replaces the saturated air by dry air and evaporation continues.
We divide both sides of the equation by to find that the mass evaporated per unit time is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?