| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
There are many different types of polymers. Some are organic, while others are inorganic. Organic polymers can be broadly grouped into either synthetic/semi-synthetic (artificial) or biological (natural) polymers. We are going to take a look at two groups of organic polymers: plastics , which are usually synthetic or semi-synthetic and biological macromolecules which are natural polymers. Both of these groups of polymers play a very important role in our lives.
In today's world, we can hardly imagine life without plastic. From cellphones to food packaging, fishing line to plumbing pipes, compact discs to electronic equipment, plastics have become a very important part of our daily lives. "Plastics" cover a range of synthetic and semi-synthetic organic polymers. Their name comes from the fact that they are 'malleable', in other words their shape can be changed and moulded.
Plastic covers a range of synthetic or semisynthetic organic polymers. Plastics may contain other substances to improve their performance. Their name comes from the fact that many of them are malleable, in other words they have the property of plasticity.
It was only in the nineteenth century that it was discovered that plastics could be made by chemically changing natural polymers. For centuries before this, only natural organic polymers had been used. Examples of natural organic polymers include waxes from plants, cellulose (a plant polymer used in fibres and ropes) and natural rubber from rubber trees. But in many cases, these natural organic polymers didn't have the characteristics that were needed for them to be used in specific ways. Natural rubber for example, is sensitive to temperature and becomes sticky and smelly in hot weather and brittle in cold weather.
In 1834 two inventors, Friedrich Ludersdorf of Germany and Nathaniel Hayward of the US, independently discovered that adding sulfur to raw rubber helped to stop the material from becoming sticky. After this, Charles Goodyear discovered that heating this modified rubber made it more resistant to abrasion, more elastic and much less sensitive to temperature. What these inventors had done was to improve the properties of a natural polymer so that it could be used in new ways. An important use of rubber now is in vehicle tyres, where these properties of rubber are critically important.
The first true plastic (i.e. one that was not based on any material found in nature) was Bakelite , a cheap, strong and durable plastic. Some of these plastics are still used for example in electronic circuit boards, where their properties of insulation and heat resistance are very important.
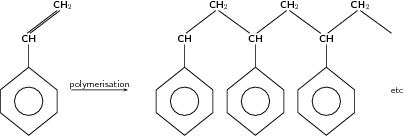
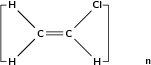
There is such a variety of different plastics available, each having their own specific properties and uses. The following are just a few examples.
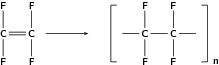

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?