| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
As its name suggests, a macromolecule is a large molecule that forms when lots of smaller molecules are joined together. In this chapter, we will be taking a closer look at the structure and properties of different macromolecules, and at how they form.
Some macromolecules are made up of lots of repeating structural units called monomers . To put it more simply, a monomer is like a building block. When lots of similar monomers are joined together by covalent bonds, they form a polymer . In an organic polymer , the monomers are joined by the carbon atoms of the polymer 'backbone'. A polymer can also be inorganic , in which case there may be atoms such as silicon in the place of carbon atoms. The key feature that makes a polymer different from other macromolecules, is the repetition of identical or similar monomers in the polymer chain. The examples shown below will help to make these concepts clearer.
Polymer is a term used to describe large molecules consisting of repeating structural units, or monomers, connected by covalent chemical bonds.
Polymers are formed through a process called polymerisation , where monomer molecules react together to form a polymer chain. Two types of polymerisation reactions are addition polymerisation and condensation polymerisation .
In chemistry, polymerisation is a process of bonding monomers, or single units together through a variety of reaction mechanisms to form longer chains called polymers.
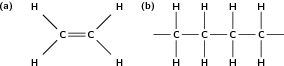
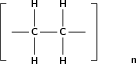
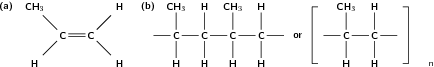
In this type of reaction, monomer molecules are added to a growing polymer chain one at a time. No small molecules are eliminated in the process. An example of this type of reaction is the formation of polyethene from ethene (fig [link] ). When molecules of ethene are joined to each other, the only thing that changes is that the double bond between the carbon atoms in each ethene monomer is replaced by a single bond so that a new carbon-carbon bond can be formed with the next monomer in the chain. In other words, the monomer is an unsaturated compound which, after an addition reaction, becomes a saturated compound.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?