| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A biological macromolecule is one that is found in living organisms. Biological macromolecules include molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids. Lipids are also biological macromolecules. They are essential for all known forms of life to survive.
A biological macromolecule is a polymer that occurs naturally in living organisms. These molecules are essential to the survival of life.
Carbohydrates include the sugars and their polymers. One key characteristic of the carbohydrates is that they contain only the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. In the carbohydrate monomers, every carbon except one has a hydroxyl group attached to it, and the remaining carbon atom is double bonded to an oxygen atom to form a carbonyl group. One of the most important monomers in the carbohydrates is glucose ( [link] ). The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) and ring (cyclic) form.
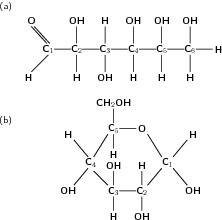
Glucose is produced during photosynthesis , which takes place in plants. During photosynthesis, sunlight (solar energy), water and carbon dioxide are involved in a chemical reaction that produces glucose and oxygen. This glucose is stored in various ways in the plant.
The photosynthesis reaction is as follows:
Glucose is an important source of energy for both the plant itself, and also for the other animals and organisms that may feed on it. Glucose plays a critical role in cellular respiration , which is a chemical reaction that occurs in the cells of all living organisms. During this reaction, glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide, water and Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). ATP is a molecule that cells use for energy so that the body's cells can function normally. The purpose of eating then, is to obtain glucose which the body can then convert into the ATP it needs to be able to survive.
The reaction for cellular respiration is as follows:
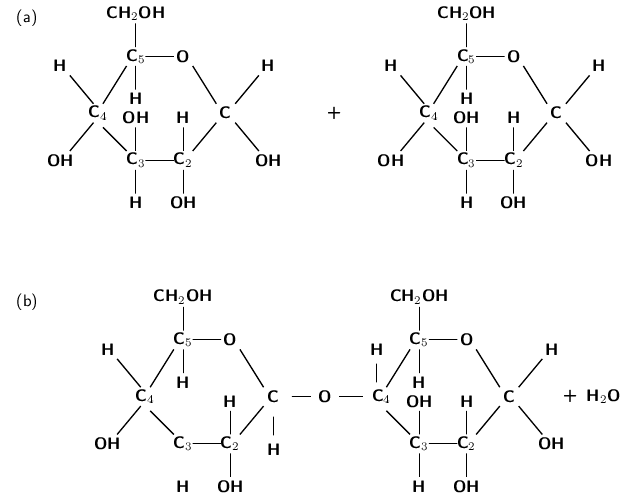
We don't often eat glucose in its simple form. More often, we eat complex carbohydrates that our bodies have to break down into individual glucose molecules before they can be used in cellular respiration. These complex carbohydrates are polymers, which form through condensation polymerisation reactions ( [link] ). Starch and cellulose are two example of carbohydrates that are polymers composed of glucose monomers.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?