| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A laser is a device that produces a special type of light: all the laser photons are identical! They all have the same wavelength (and frequency), amplitude and phase. Since they all have the same wavelength, this means they all have the same colour and the light is called monochromatic . ( Note: mono means "one" or "single" and chromatic means "colour".) This is very different to most other light sources which produce light with a range of wavelengths (e.g. white light from the sun consists of all the visible wavelengths.)
Laser light is highly directional and can be focused very well. This focus allows laser beams to be used over long distances, and to pack a lot of energy into the beam while still requiring reasonably small amounts of energy to be generated. Each centimetre of a typical laser beam contains many billions of photons. These special properties of laser light come from the way in which the laser photons are created and the energy levels of the material that makes up the laser. These properties make laser light extremely useful in many applications from CD players to eye surgery.
The term LASER stands for L ight A mplification by the S timulated E mission of R adiation. This stimulated emission is different to the spontaneous emission already discussed earlier. Let's review the absorption and emission processes which can occur in atoms.
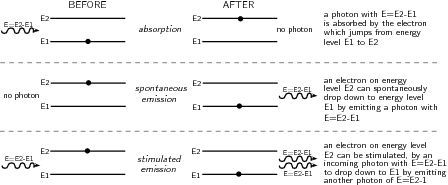
Spontaneous emission occurs when an atom is in an unstable excited state and randomly decays to a less energetic state, emitting a photon to carry off the excess energy. The unstable state decays in a characteristic time, called the lifetime.
A meta-stable state is an excited atomic state that has an unusually long lifetime, compared to the lifetimes of other excited states of that atom. While most excited states have lifetimes measured in microseconds and nanoseconds ( s and s), meta-stable states can have lifetimes of milliseconds ( s) or even seconds.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?