| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the alkenes, there is at least one double bond between two carbon atoms. This means that they are unsaturated and are more reactive than the alkanes. The simplest alkene is ethene (also known as ethylene), which is shown in [link] .
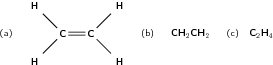
As with the alkanes, the alkenes also form a homologous series. They have the general formula C H . The second alkene in the series would therefore be C H . This molecule is known as propene ( [link] ). Note that if an alkene has two double bonds, it is called a diene and if it has three double bonds it is called a triene .
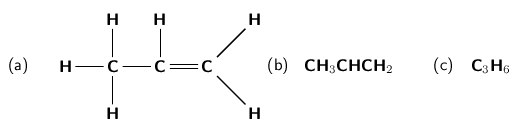
The alkenes have a variety of uses. Ethylene for example is a hormone in plants that stimulates the ripening of fruits and the opening of flowers. Propene is an important compound in the petrochemicals industry. It is used as a monomer to make polypropylene and is also used as a fuel gas for other industrial processes.
Similar rules will apply in naming the alkenes, as for the alkanes.
Khan academy video on alkenes
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound:
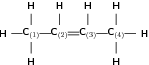
The compound is an alkene and will have the suffix -ene.
There are four carbon atoms in the longest chain and so the prefix for this compound will be 'but'.
Remember that when there is a double or triple bond, the carbon atoms must be numbered so that the double or triple bond is at the lowest numbered carbon. In this case, it doesn't matter whether we number the carbons from the left to right, or from the right to left. The double bond will still fall between C and C . The position of the bond will come just before the suffix in the compound's name.
There are no branched groups in this molecule.
The name of this compound is but-2-ene .
Draw the structural formula for the organic compound 3-methyl-butene
The suffix -ene means that this compound is an alkene and there must be a double bond in the molecule. There is no number immediately before the suffix which means that the double bond must be at the first carbon in the chain.
The prefix for the compound is 'but' so there must be four carbons in the longest chain.
There is a methyl group at the third carbon atom in the chain.
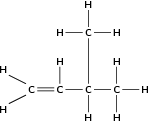
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound:
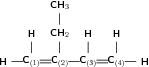
The compound is an alkene and will have the suffix -ene. There is a double bond between the first and second carbons and also between the third and forth carbons. The organic compound is therefore a 'diene'.
There are four carbon atoms in the longest chain and so the prefix for this compound will be 'but'. The carbon atoms are numbered 1 to 4 in the diagram above. Remember that the main carbon chain must contain both the double bonds.
There is an ethyl group on the second carbon.
The name of this compound is 2-ethyl-but-1,3-diene .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?