| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When you look at the matter, or physical substances, around you, you will realise that atoms seldom exist on their own. More often, the things around us are made up of different atoms that have been joined together. This is called chemical bonding . Chemical bonding is one of the most important processes in chemistry because it allows all sorts of different molecules and combinations of atoms to form, which then make up the objects in the complex world around us. There are, however, some atoms that do exist on their own, and which do not bond with others. The noble gases in Group 8 of the Periodic Table behave in this way. They include elements like neon (Ne), helium (He) and argon (Ar). The important question then is, why do some atoms bond but others do not?
As we begin this section, it's important to remember that what we will go on to discuss is a model of bonding, that is based on a particular model of the atom. You will remember from the discussion on atoms that a model is a representation of what is happening in reality. In the model of the atom that you are familiar with, the atom is made up of a central nucleus, surrounded by electrons that are arranged in fixed energy levels (sometimes called shells ). Within each energy level, electrons move in orbitals of different shapes. The electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom are called the valence electrons . This model of the atom is useful in trying to understand how different types of bonding take place between atoms.
You will remember from these earlier discussions of electrons and energy levels in the atom, that electrons always try to occupy the lowest possible energy level. In the same way, an atom also prefers to exist in the lowest possible energy state so that it is most stable . An atom is most stable when all its valence electron orbitals are full . In other words, the outer energy level of the atom contains the maximum number of electrons that it can. A stable atom is also an unreactive one, and is unlikely to bond with other atoms. This explains why the noble gases are unreactive and why they exist as atoms, rather than as molecules. Look for example at the electron configuration of neon (1s 2s 2p ). Neon has eight valence electrons in its valence energy shell. This is the maximum that it can hold and so neon is very stable and unreactive, and will not form new bonds. Other atoms, whose valence energy levels are not full, are more likely to bond in order to become more stable. We are going to look a bit more closely at some of the energy changes that take place when atoms bond.
Let's start by imagining that there are two hydrogen atoms approaching one another. As they move closer together, there are three forces that act on the atoms at the same time. These forces are shown in [link] and are described below:
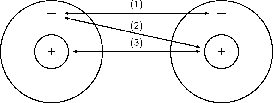
Now look at [link] to understand the energy changes that take place when the two atoms move towards each other.
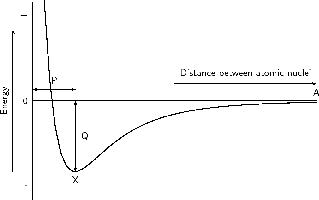
In the example of the two hydrogen atoms, where the resultant force between them is attraction, the energy of the system is zero when the atoms are far apart (point A), because there is no interaction between the atoms. When the atoms move closer together, attractive forces dominate and the atoms are pulled towards each other. As this happens, the potential energy of the system decreases because energy would now need to be supplied to the system in order to move the atoms apart. However, as the atoms continue to move closer together (i.e. left along the horizontal axis of the graph), repulsive forces start to dominate and this causes the potential energy of the system to rise again. At some point, the attractive and repulsive effects are balanced, and the energy of the system is at its minimum (point X). It is at this point, when the energy is at a minimum, that bonding takes place.
The distance marked 'P' is the bond length , i.e. the distance between the nuclei of the atoms when they bond. 'Q' represents the bond energy i.e. the amount of energy that must be added to the system to break the bonds that have formed. Bond strength means how strongly one atom attracts and is held to another. The strength of a bond is related to the bond length, the size of the bonded atoms and the number of bonds between the atoms. In general, the shorter the bond length, the stronger the bond between the atoms, and the smaller the atoms involved, the stronger the bond. The greater the number of bonds between the atoms, the greater the bond strength.
A chemical bond is formed when atoms are held together by attractive forces. This attraction occurs when electrons are shared between atoms, or when electrons are exchanged between the atoms that are involved in the bond. The sharing or exchange of electrons takes place so that the outer energy levels of the atoms involved are filled and the atoms are more stable. If an electron is shared , it means that it will spend its time moving in the electron orbitals around both atoms. If an electron is exchanged it means that it is transferred from one atom to another, in other words one atom gains an electron while the other loses an electron.
A chemical bond is the physical process that causes atoms and molecules to be attracted to each other, and held together in more stable chemical compounds.
The type of bond that is formed depends on the elements that are involved. In this section, we will be looking at three types of chemical bonding: covalent , ionic and metallic bonding .
You need to remember that it is the valence electrons that are involved in bonding and that atoms will try to fill their outer energy levels so that they are more stable.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?