| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
You should have found this formula:
Here, is the number of nodes. is the length of the string. The frequency is:
Here, is the velocity of the wave. This may seem confusing. The wave is a standing wave, so how can it have a velocity? But one standing wave is made up of many waves that travel back and forth on the string.Each of these waves has the same velocity. This speed depends on the mass and tension of the string.
We have a standing wave on a string that is 65 cm long. The wave has a velocity of 143 m.s . Find the frequencies of the fundamental, first, second, and third harmonics.
To find the frequency we will use
To find we need the wavelength of each harmonic ( ). The wavelength is then substituted into to find the harmonics. The table below shows the calculations.
110 Hz is the natural frequency of the A string on a guitar. The third harmonic, at 440 Hz, is the note that orchestras use for tuning.
Guitars use strings with high tension. The length, tension and mass of the strings affect the pitches you hear.High tension and short strings make high frequencies; low tension and long strings make low frequencies. When a string is first plucked, it vibrates at many frequencies.All of these except the harmonics are quickly filtered out. The harmonics make up the tone we hear.
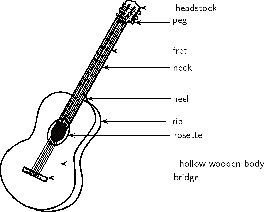
The body of a guitar acts as a large wooden soundboard. Here is how a soundboard works: the body picks up the vibrations of the strings. It then passes these vibrations to the air.A sound hole allows the soundboard of the guitar to vibrate more freely. It also helps sound waves to get out of the body.
The neck of the guitar has thin metal bumps on it called frets. Pressing a string against a fret shortens the length of that string.This raises the natural frequency and the pitch of that string.
Most guitars use an "equal tempered" tuning of 12 notes per octave. A 6 string guitar has a range of 4 octaves with pitches from 82.407 Hz (low E) to 2093 kHz (high C). Harmonics may reach over 20 kHz, in the inaudible range.
Let us look at another stringed instrument: the piano. The piano has strings that you cannot see. When a key is pressed, a felt-tipped hammer hits astring inside the piano. The pitch depends on the length, tension and mass of the string. But there are many more strings than keys on a piano. This is because the short and thinstrings are not as loud as the long and heavy strings. To make up for this, the higher keys have groups of two to four strings each.
The soundboard in a piano is a large cast iron plate. It picks up vibrations from the strings. This heavy plate can withstand over 200 tons of pressure from string tension!Its mass also allows the piano to sustain notes for long periods of time.
The piano has a wide frequency range, from 27,5 Hz (low A) to 4186,0 Hz (upper C). But these are just the fundamental frequencies. A piano plays complex,rich tones with over 20 harmonics per note. Some of these are out of the range of human hearing. Very low piano notes can be heard mostly because of their higher harmonics.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?