| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
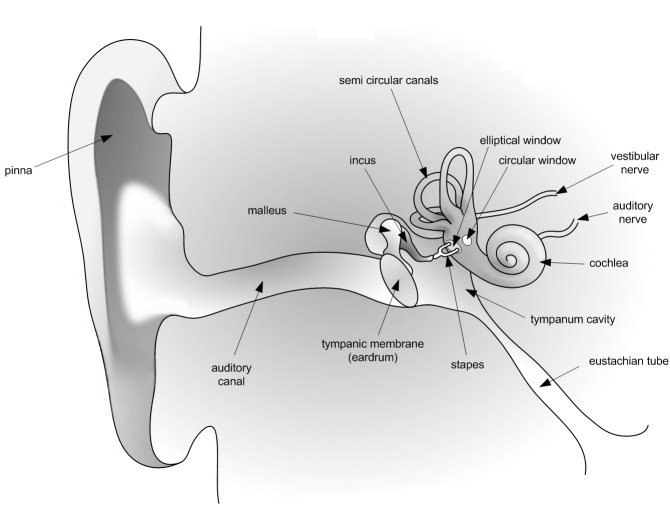
The human ear is divided into three main sections: the outer, middle, and inner ear. Let's follow the journey of a sound wave from the pinna (outermost part) to the auditory nerve (innermost part) which transmits a signal to the brain. The pinna is the part of the ear we typically think of when we refer to the ear. Its mainfunction is to collect and focus an incident sound wave. The wave then travels through the ear canal until it meets the eardrum. Thepressure fluctuations of the sound wave make the eardrum vibrate. The three very small bones of the middle ear, the malleus (hammer),the incus (anvil), and the stapes (stirrup), transmit the signal through to the elliptical window. The elliptical window is the beginning of theinner ear. From the elliptical window the sound waves are transmitted through the liquid in the inner ear and interpreted as sounds by the brain.The inner ear, made of the semicircular canals, the cochlea, and the auditory nerve, is filled with fluid. The fluid allows the body todetect quick movements and maintain balance. The snail-shaped cochlea is covered in nerve cells. There are more than 25 000 hairlikenerve cells. Different nerve cells vibrate with different frequencies. When a nerve cell vibrates, it releases electrical impulsesto the auditory nerve. The impulses are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve and understood as sound.
Intensity is one indicator of amplitude. Intensity is the energy transmitted over a unit of area each second.
Intensity is defined as:
By the definition of intensity, we can see that the units of intensity are
The unit of intensity is the decibel (symbol: dB). This reduces to an SI equivalent of .
The average threshold of hearing is . Below this intensity, the sound is too soft for the ear to hear. The threshold of pain is . Above this intensity a sound is so loud it becomes uncomfortable for the ear.
Notice that there is a factor of between the thresholds of hearing and pain. This is one reason we define the decibel (dB) scale.
The intensity in dB of a sound of intensity , is given by:
In this way we can compress the whole hearing intensity scale into a range from 0 dB to 120 dB.
| Source | Intensity (dB) | Times greater than hearing threshold |
| Rocket Launch | 180 | |
| Jet Plane | 140 | |
| Threshold of Pain | 120 | |
| Rock Band | 110 | |
| Subway Train | 90 | |
| Factory | 80 | |
| City Traffic | 70 | |
| Normal Conversation | 60 | |
| Library | 40 | |
| Whisper | 20 | |
| Threshold of hearing | 0 | 0 |
Notice that there are sounds which exceed the threshold of pain. Exposure to these sounds can cause immediate damage to hearing.In fact, exposure to sounds from 80 dB and above can damage hearing over time. Measurescan be taken to avoid damage, such as wearing earplugs or ear muffs. Limiting exposure time andincreasing distance between you and the source are also important steps for protecting your hearing.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?