| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This demonstration shows that:
You will need:
You will have to:
You now have a working model of the human eye.
Tasks
Eyesight begins with lenses. As light rays enter your eye, they pass first through the cornea and then through the crystalline lens . These form a double lens system and focus light rays onto the back wall of the eye, called the retina . Rods and cones are nerve cells on the retina that transform light into electrical signals. These signals are sent to the brain via the optic nerve . A cross-section of the eye is shown in [link] .

For clear vision, the image must be formed right on the retina, not in front of or behind it. To accomplish this, you may need a long or short focal length, depending on the object distance. How do we get the exact right focal length we need? Remember that the lens system has two parts. The cornea is fixed in place but the crystalline lens is flexible – it can change shape. When the shape of the lens changes, its focal length also changes. You have muscles in your eye called ciliary muscles that control the shape of the crystalline lens. When you focus your gaze on something, you are squeezing (or relaxing) these muscles. This process of accommodation changes the focal length of the lens and allows you to see an image clearly.
The lens in the eye creates a real image that is smaller than the object and is inverted
( [link] ).
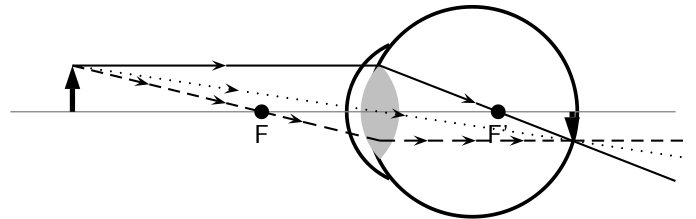
In a normal eye the image is focused on the retina.

If the muscles in the eye are unable to accommodate adequately, the image will not be in focus. This leads to problems with vision. There are three basic conditions that arise:
Short-sightedness or myopia is a defect of vision which means that the image is focused in front of the retina. Close objects are seen clearly but distant objects appear blurry. This condition can be corrected by placing a diverging lens in front of the eye. The diverging lens spreads out light rays before they enter the eye. The situation for short-sightedness and how to correct it is shown in [link] .


Long-sightedness or hyperopia is a defect of vision which means that the image is focused in behind the retina. People with this condition can see distant objects clearly, but not close ones. A converging lens in front of the eye corrects long-sightedness by converging the light rays slightly before they enter the eye. Reading glasses are an example of a converging lens used to correct long-sightedness.


Astigmatism is characterised by a cornea or lens that is not spherical, but is more curved in one plane compared to another. This means that horizontal lines may be focused at a different point to vertical lines. Astigmatism causes blurred vision and is corrected by a special lens, which has different focal lengths in the vertical and horizontal planes.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?