| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
According to Newton I, things 'like to keep on doing what they are doing'. In other words, if an object is moving, it tends to continue moving (in a straight line and at the same speed) and if an object is stationary, it tends to remain stationary. So how do objects start moving?
Let us look at the example of a 10 kg box on a rough table. If we push lightly on the box as indicated in the diagram, the box won't move. Let's say we applied a force of 100 N, yet the box remains stationary. At this point a frictional force of 100 N is acting on the box, preventing the box from moving. If we increase the force, let's say to 150 N and the box almost starts to move, the frictional force is 150 N. To be able to move the box, we need to push hard enough to overcome the friction and then move the box. If we therefore apply a force of 200 N remembering that a frictional force of 150 N is present, the 'first' 150 N will be used to overcome or 'cancel' the friction and the other 50 N will be used to move (accelerate) the block. In order to accelerate an object we must have a resultant force acting on the block.
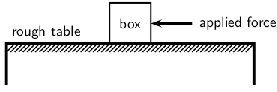
Now, what do you think will happen if we pushed harder, lets say 300 N? Or, what do you think will happen if the mass of the block was more, say 20 kg, or what if it was less? Let us investigate how the motion of an object is affected by mass and force.
Aim:
To investigate the relation between the acceleration of objects and the application of a constant resultant force.
Method:
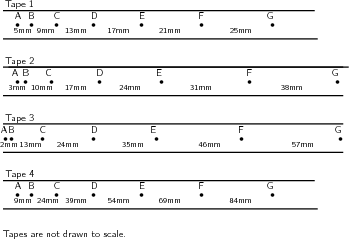
Instructions:
You will have noted in the investigation above that the heavier the trolley is, the slower it moved. The acceleration is inversely proportional to the mass. In mathematical terms:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?