| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When these two waves exist in the same medium, the resultant wave resulting from the superposition of the two individual waves is the sum of the two individual waves:
The resultant wave can be better understood by using the trigonometric identity:
where and . The resulting wave becomes
This equation is usually written as
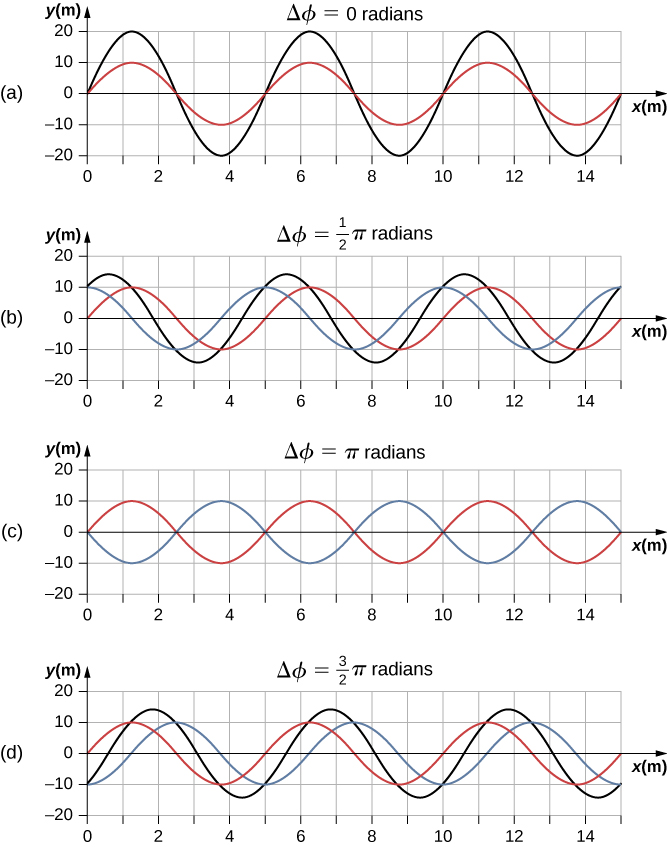
The resultant wave has the same wave number and angular frequency, an amplitude of and a phase shift equal to half the original phase shift. Examples of waves that differ only in a phase shift are shown in [link] . The red and blue waves each have the same amplitude, wave number, and angular frequency, and differ only in a phase shift. They therefore have the same period, wavelength, and frequency. The green wave is the result of the superposition of the two waves. When the two waves have a phase difference of zero, the waves are in phase, and the resultant wave has the same wave number and angular frequency, and an amplitude equal to twice the individual amplitudes (part (a)). This is constructive interference. If the phase difference is the waves interfere in destructive interference (part (c)). The resultant wave has an amplitude of zero. Any other phase difference results in a wave with the same wave number and angular frequency as the two incident waves but with a phase shift of and an amplitude equal to Examples are shown in parts (b) and (d).
An incident sinusoidal wave is sent along a string that is fixed to the wall with a wave speed of v . The wave reflects off the end of the string. Describe the reflected wave.
A string of a length of 2.00 m with a linear mass density of is attached to the end of a 2.00-m-long string with a linear mass density of The free end of the higher-density string is fixed to the wall, and a student holds the free end of the low-density string, keeping the tension constant in both strings. The student sends a pulse down the string. Describe what happens at the interface between the two strings.
At the interface, the incident pulse produces a reflected pulse and a transmitted pulse. The reflected pulse would be out of phase with respect to the incident pulse, and would move at the same propagation speed as the incident pulse, but would move in the opposite direction. The transmitted pulse would travel in the same direction as the incident pulse, but at half the speed. The transmitted pulse would be in phase with the incident pulse. Both the reflected pulse and the transmitted pulse would have amplitudes less than the amplitude of the incident pulse.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?