| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Check Your Understanding Two blocks are at rest and in contact on a frictionless surface as shown below, with and applied force 24 N. (a) Find the acceleration of the system of blocks. (b) Suppose that the blocks are later separated. What force will give the second block, with the mass of 6.0 kg, the same acceleration as the system of blocks?
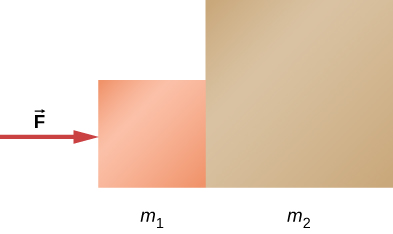
a. ; b. 18 N
View this video to watch examples of action and reaction.
View this video to watch examples of Newton’s laws and internal and external forces.
Identify the action and reaction forces in the following situations: (a) Earth attracts the Moon, (b) a boy kicks a football, (c) a rocket accelerates upward, (d) a car accelerates forward, (e) a high jumper leaps, and (f) a bullet is shot from a gun.
a. action: Earth pulls on the Moon, reaction: Moon pulls on Earth; b. action: foot applies force to ball, reaction: ball applies force to foot; c. action: rocket pushes on gas, reaction: gas pushes back on rocket; d. action: car tires push backward on road, reaction: road pushes forward on tires; e. action: jumper pushes down on ground, reaction: ground pushes up on jumper; f. action: gun pushes forward on bullet, reaction: bullet pushes backward on gun.
Suppose that you are holding a cup of coffee in your hand. Identify all forces on the cup and the reaction to each force.
(a) Why does an ordinary rifle recoil (kick backward) when fired? (b) The barrel of a recoilless rifle is open at both ends. Describe how Newton’s third law applies when one is fired. (c) Can you safely stand close behind one when it is fired?
a. The rifle (the shell supported by the rifle) exerts a force to expel the bullet; the reaction to this force is the force that the bullet exerts on the rifle (shell) in opposite direction. b. In a recoilless rifle, the shell is not secured in the rifle; hence, as the bullet is pushed to move forward, the shell is pushed to eject from the opposite end of the barrel. c. It is not safe to stand behind a recoilless rifle.
(a) What net external force is exerted on a 1100.0-kg artillery shell fired from a battleship if the shell is accelerated at (b) What is the magnitude of the force exerted on the ship by the artillery shell, and why?
a. b. The force exerted on the ship is also because it is opposite the shell’s direction of motion.
A brave but inadequate rugby player is being pushed backward by an opposing player who is exerting a force of 800.0 N on him. The mass of the losing player plus equipment is 90.0 kg, and he is accelerating backward at . (a) What is the force of friction between the losing player’s feet and the grass? (b) What force does the winning player exert on the ground to move forward if his mass plus equipment is 110.0 kg?
A history book is lying on top of a physics book on a desk, as shown below; a free-body diagram is also shown. The history and physics books weigh 14 N and 18 N, respectively. Identify each force on each book with a double subscript notation (for instance, the contact force of the history book pressing against physics book can be described as ), and determine the value of each of these forces, explaining the process used.
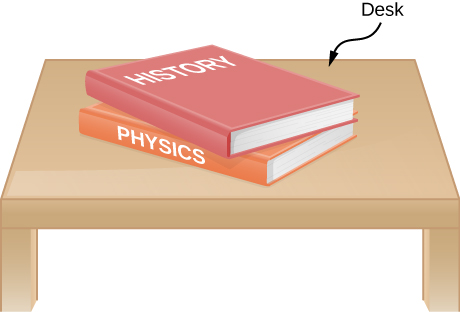
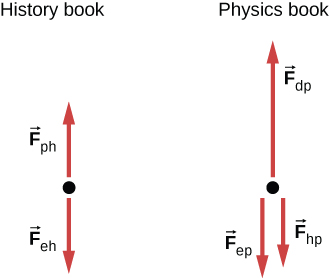
Because the weight of the history book is the force exerted by Earth on the history book, we represent it as Aside from this, the history book interacts only with the physics book. Because the acceleration of the history book is zero, the net force on it is zero by Newton’s second law: where is the force exerted by the physics book on the history book. Thus, We find that the physics book exerts an upward force of magnitude 14 N on the history book. The physics book has three forces exerted on it: due to Earth, due to the history book, and due to the desktop. Since the physics book weighs 18 N, From Newton’s third law, so Newton’s second law applied to the physics book gives or so The desk exerts an upward force of 32 N on the physics book. To arrive at this solution, we apply Newton’s second law twice and Newton’s third law once.
A truck collides with a car, and during the collision, the net force on each vehicle is essentially the force exerted by the other. Suppose the mass of the car is 550 kg, the mass of the truck is 2200 kg, and the magnitude of the truck’s acceleration is . Find the magnitude of the car’s acceleration.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?