-
Home
- University physics volume 1
- Unit 1. mechanics
- Potential energy and conservation
- Conservation of energy
Systems with several particles or objects
Systems generally consist of more than one particle or object. However, the conservation of mechanical energy, in one of the forms in
[link] or
[link] , is a fundamental law of physics and applies to any system. You just have to include the kinetic and potential energies of all the particles, and the work done by all the non-conservative forces acting on them. Until you learn more about the dynamics of systems composed of many particles, in
Linear Momentum and Collisions ,
Fixed-Axis Rotation , and
Angular Momentum , it is better to postpone discussing the application of energy conservation to then.
Summary
- A conserved quantity is a physical property that stays constant regardless of the path taken.
- A form of the work-energy theorem says that the change in the mechanical energy of a particle equals the work done on it by non-conservative forces.
- If non-conservative forces do no work and there are no external forces, the mechanical energy of a particle stays constant. This is a statement of the conservation of mechanical energy and there is no change in the total mechanical energy.
- For one-dimensional particle motion, in which the mechanical energy is constant and the potential energy is known, the particle’s position, as a function of time, can be found by evaluating an integral that is derived from the conservation of mechanical energy.
Conceptual questions
When a body slides down an inclined plane, does the work of friction depend on the body’s initial speed? Answer the same question for a body sliding down a curved surface.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Consider the following scenario. A car for which friction is
not negligible accelerates from rest down a hill, running out of gasoline after a short distance (see below). The driver lets the car coast farther down the hill, then up and over a small crest. He then coasts down that hill into a gas station, where he brakes to a stop and fills the tank with gasoline. Identify the forms of energy the car has, and how they are changed and transferred in this series of events.
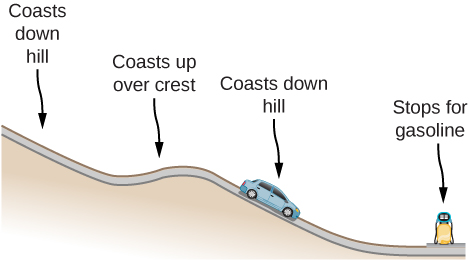
The car experiences a change in gravitational potential energy as it goes down the hills because the vertical distance is decreasing. Some of this change of gravitational potential energy will be taken away by work done by friction. The rest of the energy results in a kinetic energy increase, making the car go faster. Lastly, the car brakes and will lose its kinetic energy to the work done by braking to a stop.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
“
constant is a special case of the work-energy theorem.” Discuss this statement.
It states that total energy of the system
E is conserved as long as there are no non-conservative forces acting on the object.
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
In a common physics demonstration, a bowling ball is suspended from the ceiling by a rope.
The professor pulls the ball away from its equilibrium position and holds it adjacent to his nose, as shown below. He releases the ball so that it swings directly away from him. Does he get struck by the ball on its return swing? What is he trying to show in this demonstration?
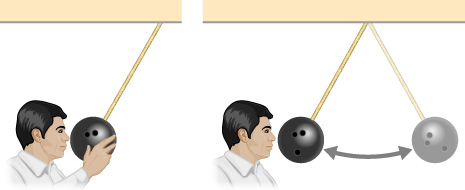
Got questions? Get instant answers now!
Questions & Answers
how does Neisseria cause meningitis
is the branch of biology that deals with the study of microorganisms.
studies of microbes
Louisiaste
when we takee the specimen which lumbar,spin,
How bacteria create energy to survive?
Bacteria doesn't produce energy they are dependent upon their substrate in case of lack of nutrients they are able to make spores which helps them to sustain in harsh environments
_Adnan
But not all bacteria make spores, l mean Eukaryotic cells have Mitochondria which acts as powerhouse for them, since bacteria don't have it, what is the substitution for it?
Muhamad
they make spores
Louisiaste
what is sporadic nd endemic, epidemic
the significance of food webs for disease transmission
Abreham
food webs brings about an infection as an individual depends on number of diseased foods or carriers dully.
Mark
explain assimilatory nitrate reduction
Assimilatory nitrate reduction is a process that occurs in some microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, in which nitrate (NO3-) is reduced to nitrite (NO2-), and then further reduced to ammonia (NH3).
Elkana
This process is called assimilatory nitrate reduction because the nitrogen that is produced is incorporated in the cells of microorganisms where it can be used in the synthesis of amino acids and other nitrogen products
Elkana
Examples of thermophilic organisms
Give Examples of thermophilic organisms
Shu
advantages of normal Flora to the host
Prevent foreign microbes to the host
Abubakar
they provide healthier benefits to their hosts
ayesha
They are friends to host only when Host immune system is strong and become enemies when the host immune system is weakened . very bad relationship!
Mark
cell is the smallest unit of life
Fauziya
cell is the smallest unit of life
Akanni
cell is the structural and functional unit of life
Hasan
is the fundamental units of Life
Musa
what are emergency diseases
There are nothing like emergency disease but there are some common medical emergency which can occur simultaneously like Bleeding,heart attack,Breathing difficulties,severe pain heart stock.Hope you will get my point .Have a nice day ❣️
_Adnan
define infection ,prevention and control
Innocent
I think infection prevention and control is the avoidance of all things we do that gives out break of infections and promotion of health practices that promote life
Lubega
Heyy Lubega hussein where are u from?
_Adnan
which site have a normal flora
Many sites of the body have it
Skin
Nasal cavity
Oral cavity
Gastro intestinal tract
Safaa
skin,Oral,Nasal,GIt
Sadik
How can Commensal can Bacteria change into pathogen?
Sadik
How can Commensal Bacteria change into pathogen?
Sadik
what are the advantages of normal Flora to the host
Micheal
what are the ways of control and prevention of nosocomial infection in the hospital
Micheal
part of a tissue or an organ being wounded or bruised.
Wilfred
what term is used to name and classify microorganisms?
Binomial nomenclature
adeolu
Got questions? Join the online conversation and get instant answers!
Source:
OpenStax, University physics volume 1. OpenStax CNX. Sep 19, 2016 Download for free at http://cnx.org/content/col12031/1.5
Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google Inc.


