| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Work , we saw that the work done on an object by the constant gravitational force, near the surface of Earth, over any displacement is a function only of the difference in the positions of the end-points of the displacement. This property allows us to define a different kind of energy for the system than its kinetic energy, which is called potential energy . We consider various properties and types of potential energy in the following subsections.
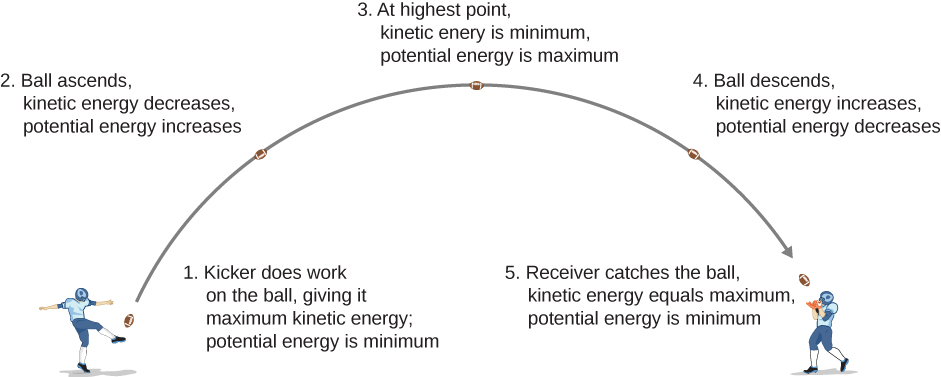
In Motion in Two and Three Dimensions , we analyzed the motion of a projectile, like kicking a football in [link] . For this example, let’s ignore friction and air resistance. As the football rises, the work done by the gravitational force on the football is negative, because the ball’s displacement is positive vertically and the force due to gravity is negative vertically. We also noted that the ball slowed down until it reached its highest point in the motion, thereby decreasing the ball’s kinetic energy. This loss in kinetic energy translates to a gain in gravitational potential energy of the football-Earth system.
As the football falls toward Earth, the work done on the football is now positive, because the displacement and the gravitational force both point vertically downward. The ball also speeds up, which indicates an increase in kinetic energy. Therefore, energy is converted from gravitational potential energy back into kinetic energy.
Based on this scenario, we can define the difference of potential energy from point A to point B as the negative of the work done:
This formula explicitly states a potential energy difference , not just an absolute potential energy. Therefore, we need to define potential energy at a given position in such a way as to state standard values of potential energy on their own, rather than potential energy differences. We do this by rewriting the potential energy function in terms of an arbitrary constant,
The choice of the potential energy at a starting location of is made out of convenience in the given problem. Most importantly, whatever choice is made should be stated and kept consistent throughout the given problem. There are some well-accepted choices of initial potential energy. For example, the lowest height in a problem is usually defined as zero potential energy, or if an object is in space, the farthest point away from the system is often defined as zero potential energy. Then, the potential energy, with respect to zero at is just

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?