| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have now seen how to calculate the average velocity between two positions. However, since objects in the real world move continuously through space and time, we would like to find the velocity of an object at any single point. We can find the velocity of the object anywhere along its path by using some fundamental principles of calculus. This section gives us better insight into the physics of motion and will be useful in later chapters.
The quantity that tells us how fast an object is moving anywhere along its path is the instantaneous velocity , usually called simply velocity . It is the average velocity between two points on the path in the limit that the time (and therefore the displacement) between the two points approaches zero. To illustrate this idea mathematically, we need to express position x as a continuous function of t denoted by x ( t ). The expression for the average velocity between two points using this notation is . To find the instantaneous velocity at any position, we let and . After inserting these expressions into the equation for the average velocity and taking the limit as , we find the expression for the instantaneous velocity:
The instantaneous velocity of an object is the limit of the average velocity as the elapsed time approaches zero, or the derivative of x with respect to t :
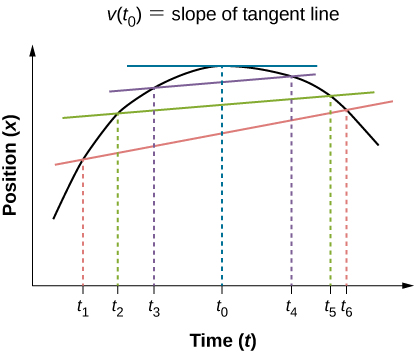
Like average velocity, instantaneous velocity is a vector with dimension of length per time. The instantaneous velocity at a specific time point is the rate of change of the position function, which is the slope of the position function at . [link] shows how the average velocity between two times approaches the instantaneous velocity at The instantaneous velocity is shown at time , which happens to be at the maximum of the position function. The slope of the position graph is zero at this point, and thus the instantaneous velocity is zero. At other times, , and so on, the instantaneous velocity is not zero because the slope of the position graph would be positive or negative. If the position function had a minimum, the slope of the position graph would also be zero, giving an instantaneous velocity of zero there as well. Thus, the zeros of the velocity function give the minimum and maximum of the position function.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?