| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The speed of a wave depends on the characteristics of the medium. For example, in the case of a guitar, the strings vibrate to produce the sound. The speed of the waves on the strings, and the wavelength, determine the frequency of the sound produced. The strings on a guitar have different thickness but may be made of similar material. They have different linear densities , where the linear density is defined as the mass per length,
In this chapter, we consider only string with a constant linear density. If the linear density is constant, then the mass of a small length of string is For example, if the string has a length of 2.00 m and a mass of 0.06 kg, then the linear density is If a 1.00-mm section is cut from the string, the mass of the 1.00-mm length is The guitar also has a method to change the tension of the strings. The tension of the strings is adjusted by turning spindles, called the tuning pegs, around which the strings are wrapped. For the guitar, the linear density of the string and the tension in the string determine the speed of the waves in the string and the frequency of the sound produced is proportional to the wave speed.
To see how the speed of a wave on a string depends on the tension and the linear density, consider a pulse sent down a taut string ( [link] ). When the taut string is at rest at the equilibrium position, the tension in the string is constant. Consider a small element of the string with a mass equal to The mass element is at rest and in equilibrium and the force of tension of either side of the mass element is equal and opposite.
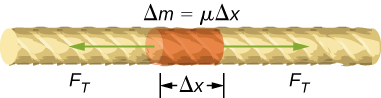
If you pluck a string under tension, a transverse wave moves in the positive x -direction, as shown in [link] . The mass element is small but is enlarged in the figure to make it visible. The small mass element oscillates perpendicular to the wave motion as a result of the restoring force provided by the string and does not move in the x -direction. The tension in the string, which acts in the positive and negative x -direction, is approximately constant and is independent of position and time.
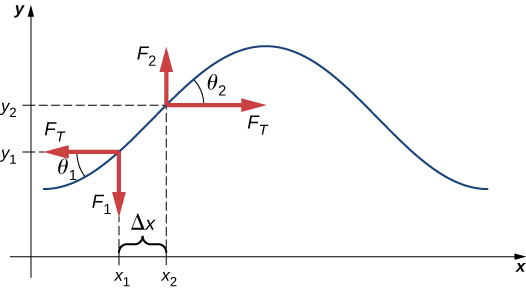
Assume that the inclination of the displaced string with respect to the horizontal axis is small. The net force on the element of the string, acting parallel to the string, is the sum of the tension in the string and the restoring force. The x -components of the force of tension cancel, so the net force is equal to the sum of the y -components of the force. The magnitude of the x -component of the force is equal to the horizontal force of tension of the string as shown in [link] . To obtain the y -components of the force, note that and The is equal to the slope of a function at a point, which is equal to the partial derivative of y with respect to x at that point. Therefore, is equal to the negative slope of the string at and is equal to the slope of the string at

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?