| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the real world, oscillations seldom follow true SHM. Friction of some sort usually acts to dampen the motion so it dies away, or needs more force to continue. In this section, we examine some examples of damped harmonic motion and see how to modify the equations of motion to describe this more general case.
A guitar string stops oscillating a few seconds after being plucked. To keep swinging on a playground swing, you must keep pushing ( [link] ). Although we can often make friction and other nonconservative forces small or negligible, completely undamped motion is rare. In fact, we may even want to damp oscillations, such as with car shock absorbers.

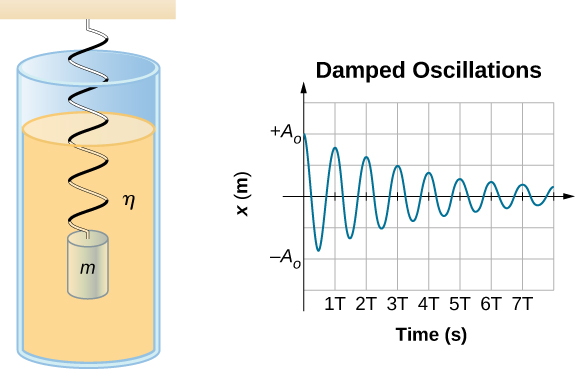
[link] shows a mass m attached to a spring with a force constant The mass is raised to a position , the initial amplitude, and then released. The mass oscillates around the equilibrium position in a fluid with viscosity but the amplitude decreases for each oscillation. For a system that has a small amount of damping, the period and frequency are constant and are nearly the same as for SHM, but the amplitude gradually decreases as shown. This occurs because the non-conservative damping force removes energy from the system, usually in the form of thermal energy.
Consider the forces acting on the mass. Note that the only contribution of the weight is to change the equilibrium position, as discussed earlier in the chapter. Therefore, the net force is equal to the force of the spring and the damping force . If the magnitude of the velocity is small, meaning the mass oscillates slowly, the damping force is proportional to the velocity and acts against the direction of motion . The net force on the mass is therefore
Writing this as a differential equation in x , we obtain
To determine the solution to this equation, consider the plot of position versus time shown in [link] . The curve resembles a cosine curve oscillating in the envelope of an exponential function where . The solution is
It is left as an exercise to prove that this is, in fact, the solution. To prove that it is the right solution, take the first and second derivatives with respect to time and substitute them into [link] . It is found that [link] is the solution if
Recall that the angular frequency of a mass undergoing SHM is equal to the square root of the force constant divided by the mass. This is often referred to as the natural angular frequency , which is represented as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?