| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When placed in a fluid, some objects float due to a buoyant force. Where does this buoyant force come from? Why is it that some things float and others do not? Do objects that sink get any support at all from the fluid? Is your body buoyed by the atmosphere, or are only helium balloons affected ( [link] )?
Answers to all these questions, and many others, are based on the fact that pressure increases with depth in a fluid. This means that the upward force on the bottom of an object in a fluid is greater than the downward force on top of the object. There is an upward force, or buoyant force , on any object in any fluid ( [link] ). If the buoyant force is greater than the object’s weight, the object rises to the surface and floats. If the buoyant force is less than the object’s weight, the object sinks. If the buoyant force equals the object’s weight, the object can remain suspended at its present depth. The buoyant force is always present, whether the object floats, sinks, or is suspended in a fluid.
The buoyant force is the upward force on any object in any fluid.
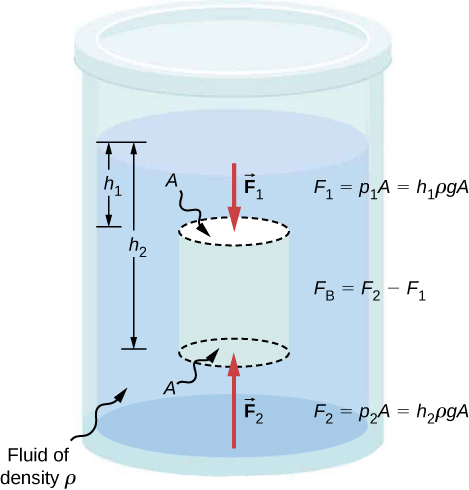
Just how large a force is buoyant force? To answer this question, think about what happens when a submerged object is removed from a fluid, as in [link] . If the object were not in the fluid, the space the object occupied would be filled by fluid having a weight This weight is supported by the surrounding fluid, so the buoyant force must equal the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
The buoyant force on an object equals the weight of the fluid it displaces. In equation form, Archimedes’ principle is
where is the buoyant force and is the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
This principle is named after the Greek mathematician and inventor Archimedes (ca. 287–212 BCE), who stated this principle long before concepts of force were well established.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?