| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The origin of Earth’s ocean tides has been a subject of continuous investigation for over 2000 years. But the work of Newton is considered to be the beginning of the true understanding of the phenomenon. Ocean tides are the result of gravitational tidal forces. These same tidal forces are present in any astronomical body. They are responsible for the internal heat that creates the volcanic activity on Io, one of Jupiter’s moons, and the breakup of stars that get too close to black holes.
If you live on an ocean shore almost anywhere in the world, you can observe the rising and falling of the sea level about twice per day. This is caused by a combination of Earth’s rotation about its axis and the gravitational attraction of both the Moon and the Sun.
Let’s consider the effect of the Moon first. In [link] , we are looking “down” onto Earth’s North Pole. One side of Earth is closer to the Moon than the other side, by a distance equal to Earth’s diameter. Hence, the gravitational force is greater on the near side than on the far side. The magnitude at the center of Earth is between these values. This is why a tidal bulge appears on both sides of Earth.
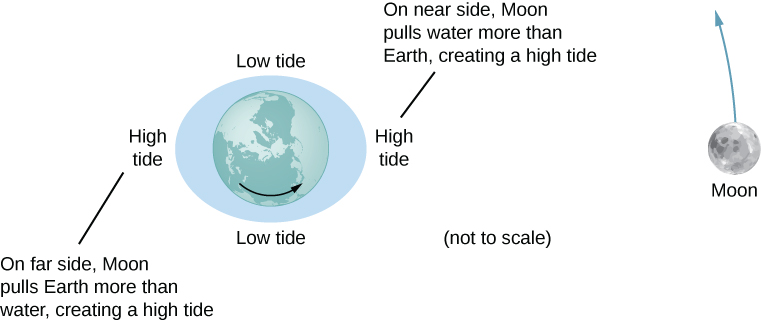
The net force on Earth causes it to orbit about the Earth-Moon center of mass, located about 1600 km below Earth’s surface along the line between Earth and the Moon. The tidal force can be viewed as the difference between the force at the center of Earth and that at any other location. In [link] , this difference is shown at sea level, where we observe the ocean tides. (Note that the change in sea level caused by these tidal forces is measured from the baseline sea level. We saw earlier that Earth bulges many kilometers at the equator due to its rotation. This defines the baseline sea level and here we consider only the much smaller tidal bulge measured from that baseline sea level.)

Why does the rise and fall of the tides occur twice per day? Look again at [link] . If Earth were not rotating and the Moon was fixed, then the bulges would remain in the same location on Earth. Relative to the Moon, the bulges stay fixed—along the line connecting Earth and the Moon. But Earth rotates (in the direction shown by the blue arrow) approximately every 24 hours. In 6 hours, the near and far locations of Earth move to where the low tides are occurring, and 6 hours later, those locations are back to the high-tide position. Since the Moon also orbits Earth approximately every 28 days, and in the same direction as Earth rotates, the time between high (and low) tides is actually about 12.5 hours. The actual timing of the tides is complicated by numerous factors, the most important of which is another astronomical body—the Sun.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?