| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Thus far in the chapter, we have extensively addressed kinematics and dynamics for rotating rigid bodies around a fixed axis. In this final section, we define work and power within the context of rotation about a fixed axis, which has applications to both physics and engineering. The discussion of work and power makes our treatment of rotational motion almost complete, with the exception of rolling motion and angular momentum, which are discussed in Angular Momentum . We begin this section with a treatment of the work-energy theorem for rotation.
Now that we have determined how to calculate kinetic energy for rotating rigid bodies, we can proceed with a discussion of the work done on a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. [link] shows a rigid body that has rotated through an angle from A to B while under the influence of a force . The external force is applied to point P , whose position is , and the rigid body is constrained to rotate about a fixed axis that is perpendicular to the page and passes through O . The rotational axis is fixed, so the vector moves in a circle of radius r , and the vector is perpendicular to
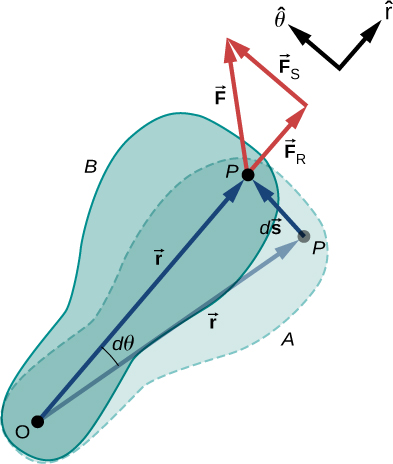
From [link] , we have
Thus,
Note that is zero because is fixed on the rigid body from the origin O to point P . Using the definition of work, we obtain
where we used the identity . Noting that , we arrive at the expression for the rotational work done on a rigid body:
The total work done on a rigid body is the sum of the torques integrated over the angle through which the body rotates . The incremental work is
where we have taken the dot product in [link] , leaving only torques along the axis of rotation. In a rigid body, all particles rotate through the same angle; thus the work of every external force is equal to the torque times the common incremental angle . The quantity is the net torque on the body due to external forces.
Similarly, we found the kinetic energy of a rigid body rotating around a fixed axis by summing the kinetic energy of each particle that makes up the rigid body. Since the work-energy theorem is valid for each particle, it is valid for the sum of the particles and the entire body.
The work-energy theorem for a rigid body rotating around a fixed axis is
where
and the rotational work done by a net force rotating a body from point A to point B is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?