| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we relate each of the rotational variables to the translational variables defined in Motion Along a Straight Line and Motion in Two and Three Dimensions . This will complete our ability to describe rigid-body rotations.
In Rotational Variables , we introduced angular variables. If we compare the rotational definitions with the definitions of linear kinematic variables from Motion Along a Straight Line and Motion in Two and Three Dimensions , we find that there is a mapping of the linear variables to the rotational ones. Linear position, velocity, and acceleration have their rotational counterparts, as we can see when we write them side by side:
| Linear | Rotational | |
|---|---|---|
| Position | x | |
| Velocity | ||
| Acceleration |
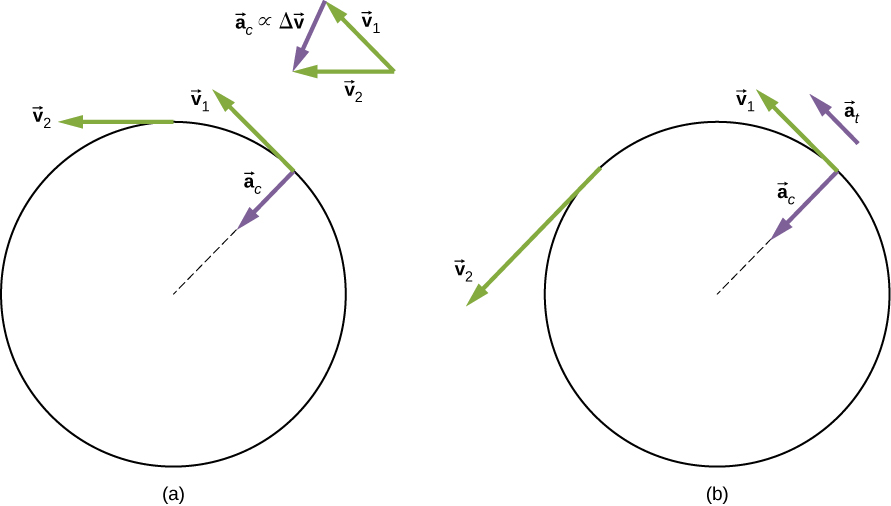
Let’s compare the linear and rotational variables individually. The linear variable of position has physical units of meters, whereas the angular position variable has dimensionless units of radians, as can be seen from the definition of , which is the ratio of two lengths. The linear velocity has units of m/s, and its counterpart, the angular velocity, has units of rad/s. In Rotational Variables , we saw in the case of circular motion that the linear tangential speed of a particle at a radius r from the axis of rotation is related to the angular velocity by the relation . This could also apply to points on a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis. Here, we consider only circular motion. In circular motion, both uniform and nonuniform, there exists a centripetal acceleration ( Motion in Two and Three Dimensions ). The centripetal acceleration vector points inward from the particle executing circular motion toward the axis of rotation. The derivation of the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration is given in Motion in Two and Three Dimensions . From that derivation, the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration was found to be
where r is the radius of the circle.
Thus, in uniform circular motion when the angular velocity is constant and the angular acceleration is zero, we have a linear acceleration—that is, centripetal acceleration—since the tangential speed in [link] is a constant. If nonuniform circular motion is present, the rotating system has an angular acceleration, and we have both a linear centripetal acceleration that is changing (because is changing) as well as a linear tangential acceleration . These relationships are shown in [link] , where we show the centripetal and tangential accelerations for uniform and nonuniform circular motion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 1' conversation and receive update notifications?