| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The bathroom scale is an excellent example of a normal force acting on a body. It provides a quantitative reading of how much it must push upward to support the weight of an object. But can you predict what you would see on the dial of a bathroom scale if you stood on it during an elevator ride? Will you see a value greater than your weight when the elevator starts up? What about when the elevator moves upward at a constant speed: will the scale still read more than your weight at rest? Consider the following example.
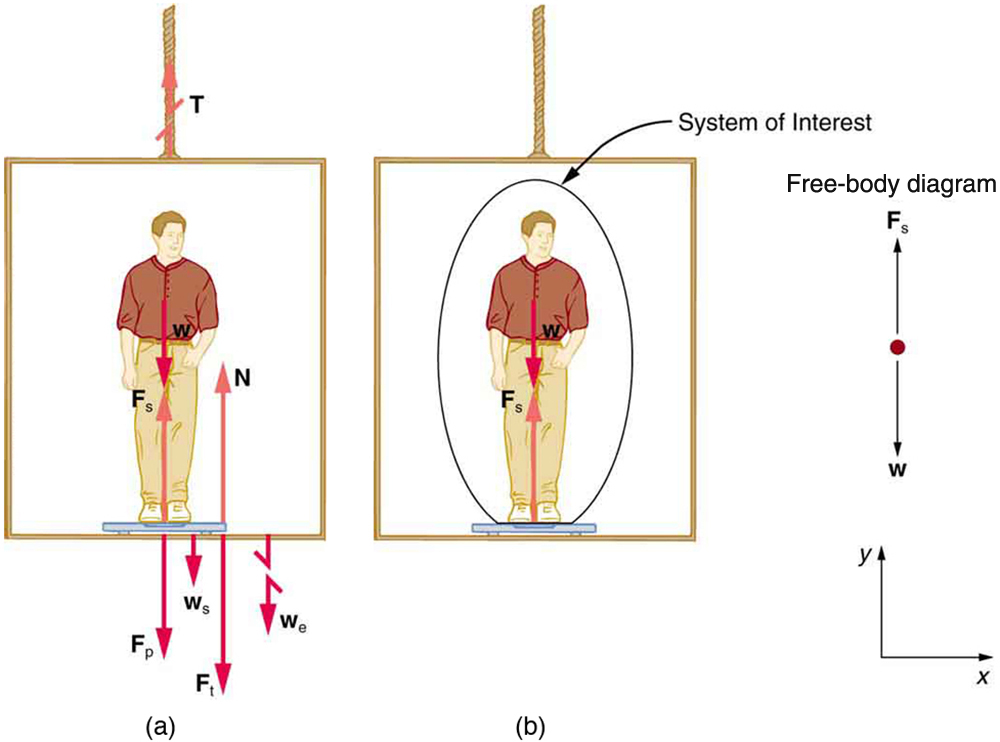
[link] shows a 75.0-kg man (weight of about 165 lb) standing on a bathroom scale in an elevator. Calculate the scale reading: (a) if the elevator accelerates upward at a rate of , and (b) if the elevator moves upward at a constant speed of 1 m/s.
Strategy
If the scale is accurate, its reading will equal , the magnitude of the force the person exerts downward on it. [link] (a) shows the numerous forces acting on the elevator, scale, and person. It makes this one-dimensional problem look much more formidable than if the person is chosen to be the system of interest and a free-body diagram is drawn as in [link] (b). Analysis of the free-body diagram using Newton’s laws can produce answers to both parts (a) and (b) of this example, as well as some other questions that might arise. The only forces acting on the person are his weight and the upward force of the scale . According to Newton’s third law and are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, so that we need to find in order to find what the scale reads. We can do this, as usual, by applying Newton’s second law,
From the free-body diagram we see that , so that
Solving for gives an equation with only one unknown:
or, because , simply
No assumptions were made about the acceleration, and so this solution should be valid for a variety of accelerations in addition to the ones in this exercise.
Solution for (a)
In this part of the problem, , so that
yielding
Discussion for (a)
This is about 185 lb. What would the scale have read if he were stationary? Since his acceleration would be zero, the force of the scale would be equal to his weight:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?