| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
or
This fundamental relationship holds for all types of waves. For water waves, is the speed of a surface wave; for sound, is the speed of sound; and for visible light, is the speed of light, for example.
Fill a large bowl or basin with water and wait for the water to settle so there are no ripples. Gently drop a cork into the middle of the bowl. Estimate the wavelength and period of oscillation of the water wave that propagates away from the cork. Remove the cork from the bowl and wait for the water to settle again. Gently drop the cork at a height that is different from the first drop. Does the wavelength depend upon how high above the water the cork is dropped?
Calculate the wave velocity of the ocean wave in [link] if the distance between wave crests is 10.0 m and the time for a sea gull to bob up and down is 5.00 s.
Strategy
We are asked to find . The given information tells us that and . Therefore, we can use to find the wave velocity.
Solution
Discussion
This slow speed seems reasonable for an ocean wave. Note that the wave moves to the right in the figure at this speed, not the varying speed at which the sea gull moves up and down.
A simple wave consists of a periodic disturbance that propagates from one place to another. The wave in [link] propagates in the horizontal direction while the surface is disturbed in the vertical direction. Such a wave is called a transverse wave or shear wave; in such a wave, the disturbance is perpendicular to the direction of propagation. In contrast, in a longitudinal wave or compressional wave, the disturbance is parallel to the direction of propagation. [link] shows an example of a longitudinal wave. The size of the disturbance is its amplitude X and is completely independent of the speed of propagation .
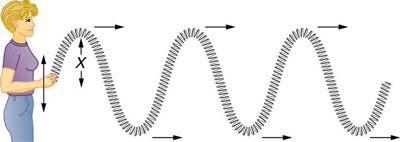
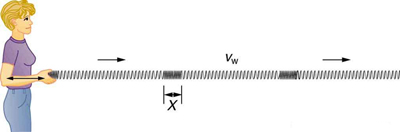
Waves may be transverse, longitudinal, or a combination of the two . (Water waves are actually a combination of transverse and longitudinal. The simplified water wave illustrated in [link] shows no longitudinal motion of the bird.) The waves on the strings of musical instruments are transverse—so are electromagnetic waves, such as visible light.
Sound waves in air and water are longitudinal. Their disturbances are periodic variations in pressure that are transmitted in fluids. Fluids do not have appreciable shear strength, and thus the sound waves in them must be longitudinal or compressional. Sound in solids can be both longitudinal and transverse.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?