| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Now consider what observer A sees happening. She sees the light from the right arriving before light from the left. Since both lamps are the same distance from her in her reference frame, from her perspective, the right flash occurred before the left flash. Here a relative velocity between observers affects whether two events are observed to be simultaneous. Simultaneity is not absolute
This illustrates the power of clear thinking. We might have guessed incorrectly that if light is emitted simultaneously, then two observers halfway between the sources would see the flashes simultaneously. But careful analysis shows this not to be the case. Einstein was brilliant at this type of thought experiment (in German, “Gedankenexperiment”). He very carefully considered how an observation is made and disregarded what might seem obvious. The validity of thought experiments, of course, is determined by actual observation. The genius of Einstein is evidenced by the fact that experiments have repeatedly confirmed his theory of relativity.
In summary: Two events are defined to be simultaneous if an observer measures them as occurring at the same time (such as by receiving light from the events). Two events are not necessarily simultaneous to all observers.
The consideration of the measurement of elapsed time and simultaneity leads to an important relativistic effect.
Time dilation is the phenomenon of time passing slower for an observer who is moving relative to another observer.
Suppose, for example, an astronaut measures the time it takes for light to cross her ship, bounce off a mirror, and return. (See [link] .) How does the elapsed time the astronaut measures compare with the elapsed time measured for the same event by a person on the Earth? Asking this question (another thought experiment) produces a profound result. We find that the elapsed time for a process depends on who is measuring it. In this case, the time measured by the astronaut is smaller than the time measured by the Earth-bound observer. The passage of time is different for the observers because the distance the light travels in the astronaut’s frame is smaller than in the Earth-bound frame. Light travels at the same speed in each frame, and so it will take longer to travel the greater distance in the Earth-bound frame.
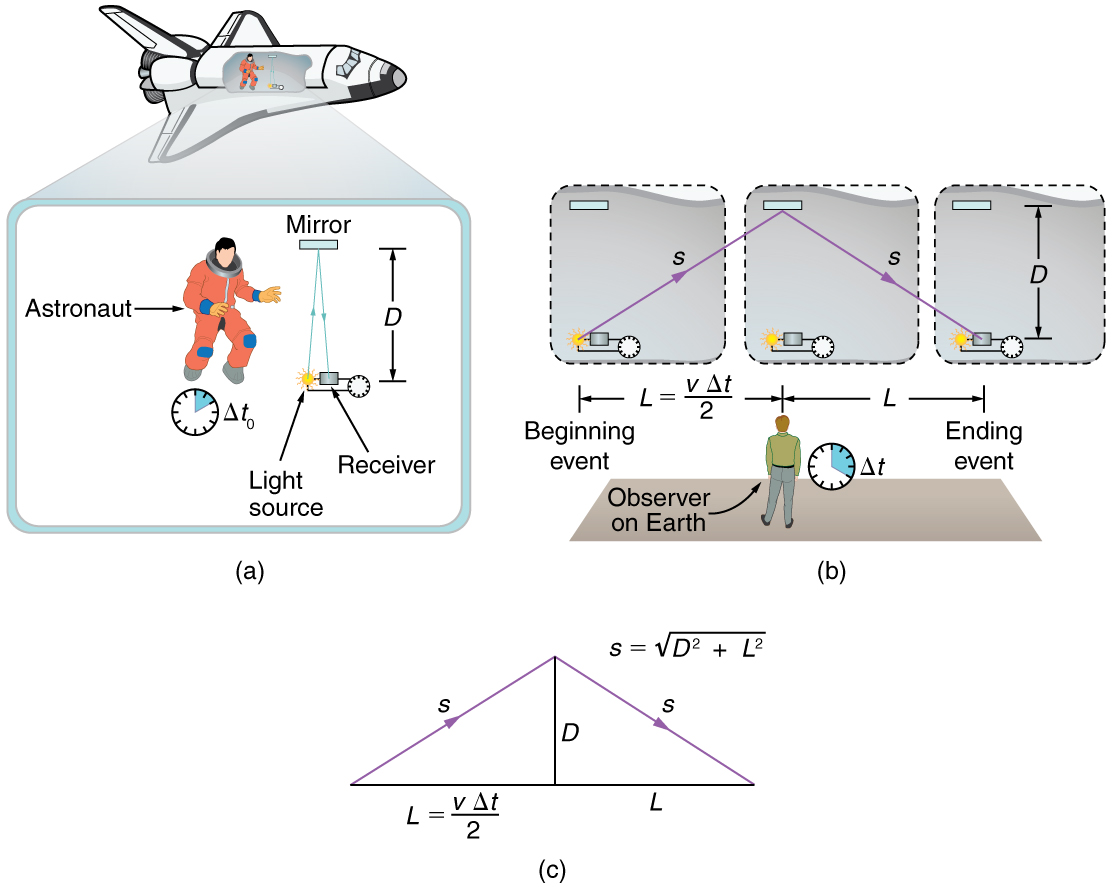
To quantitatively verify that time depends on the observer, consider the paths followed by light as seen by each observer. (See [link] (c).) The astronaut sees the light travel straight across and back for a total distance of , twice the width of her ship. The Earth-bound observer sees the light travel a total distance . Since the ship is moving at speed to the right relative to the Earth, light moving to the right hits the mirror in this frame. Light travels at a speed in both frames, and because time is the distance divided by speed, the time measured by the astronaut is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?