| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In fact, the mass and the force constant are the only factors that affect the period and frequency of simple harmonic motion.
The period of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by
and, because , the frequency of a simple harmonic oscillator is
Note that neither nor has any dependence on amplitude.
Find two identical wooden or plastic rulers. Tape one end of each ruler firmly to the edge of a table so that the length of each ruler that protrudes from the table is the same. On the free end of one ruler tape a heavy object such as a few large coins. Pluck the ends of the rulers at the same time and observe which one undergoes more cycles in a time period, and measure the period of oscillation of each of the rulers.
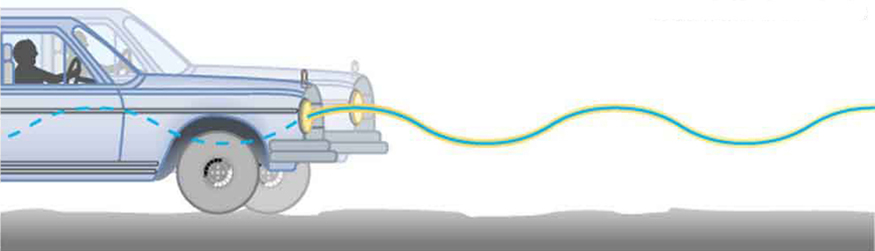
If the shock absorbers in a car go bad, then the car will oscillate at the least provocation, such as when going over bumps in the road and after stopping (See [link] ). Calculate the frequency and period of these oscillations for such a car if the car’s mass (including its load) is 900 kg and the force constant ( ) of the suspension system is .
Strategy
The frequency of the car’s oscillations will be that of a simple harmonic oscillator as given in the equation . The mass and the force constant are both given.
Solution
Discussion
The values of and both seem about right for a bouncing car. You can observe these oscillations if you push down hard on the end of a car and let go.
If a time-exposure photograph of the bouncing car were taken as it drove by, the headlight would make a wavelike streak, as shown in [link] . Similarly, [link] shows an object bouncing on a spring as it leaves a wavelike "trace of its position on a moving strip of paper. Both waves are sine functions. All simple harmonic motion is intimately related to sine and cosine waves.
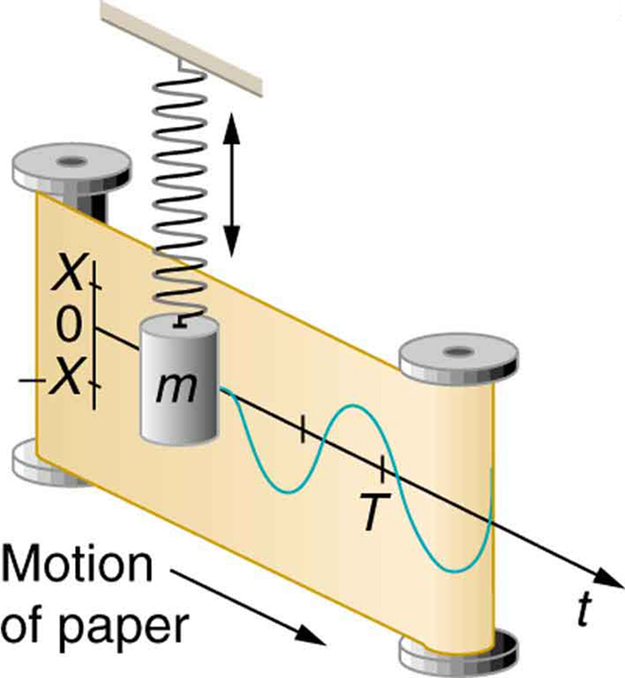
The displacement as a function of time t in any simple harmonic motion—that is, one in which the net restoring force can be described by Hooke’s law, is given by
where is amplitude. At , the initial position is , and the displacement oscillates back and forth with a period . (When , we get again because .). Furthermore, from this expression for , the velocity as a function of time is given by:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?