| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The relationships between the three common temperature scales is shown in [link] . Temperatures on these scales can be converted using the equations in [link] .
| To convert from . . . | Use this equation . . . | Also written as . . . |
|---|---|---|
| Celsius to Fahrenheit | ||
| Fahrenheit to Celsius | ||
| Celsius to Kelvin | ||
| Kelvin to Celsius | ||
| Fahrenheit to Kelvin | ||
| Kelvin to Fahrenheit |
Notice that the conversions between Fahrenheit and Kelvin look quite complicated. In fact, they are simple combinations of the conversions between Fahrenheit and Celsius, and the conversions between Celsius and Kelvin.
“Room temperature” is generally defined to be . (a) What is room temperature in ? (b) What is it in K?
Strategy
To answer these questions, all we need to do is choose the correct conversion equations and plug in the known values.
Solution for (a)
1. Choose the right equation. To convert from to , use the equation
2. Plug the known value into the equation and solve:
Solution for (b)
1. Choose the right equation. To convert from to K, use the equation
2. Plug the known value into the equation and solve:
The Reaumur scale is a temperature scale that was used widely in Europe in the 18th and 19th centuries. On the Reaumur temperature scale, the freezing point of water is and the boiling temperature is . If “room temperature” is on the Celsius scale, what is it on the Reaumur scale?
Strategy
To answer this question, we must compare the Reaumur scale to the Celsius scale. The difference between the freezing point and boiling point of water on the Reaumur scale is . On the Celsius scale it is . Therefore . Both scales start at for freezing, so we can derive a simple formula to convert between temperatures on the two scales.
Solution
1. Derive a formula to convert from one scale to the other:
2. Plug the known value into the equation and solve:
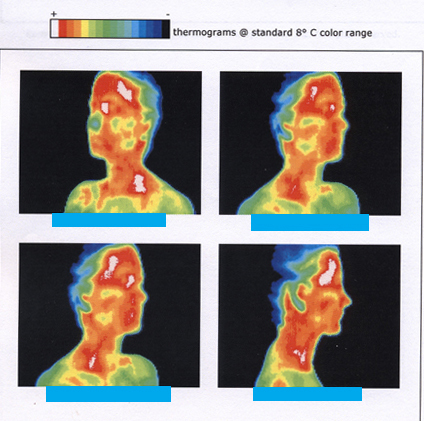
[link] shows the wide range of temperatures found in the universe. Human beings have been known to survive with body temperatures within a small range, from to to ). The average normal body temperature is usually given as ( ), and variations in this temperature can indicate a medical condition: a fever, an infection, a tumor, or circulatory problems (see [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?