| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
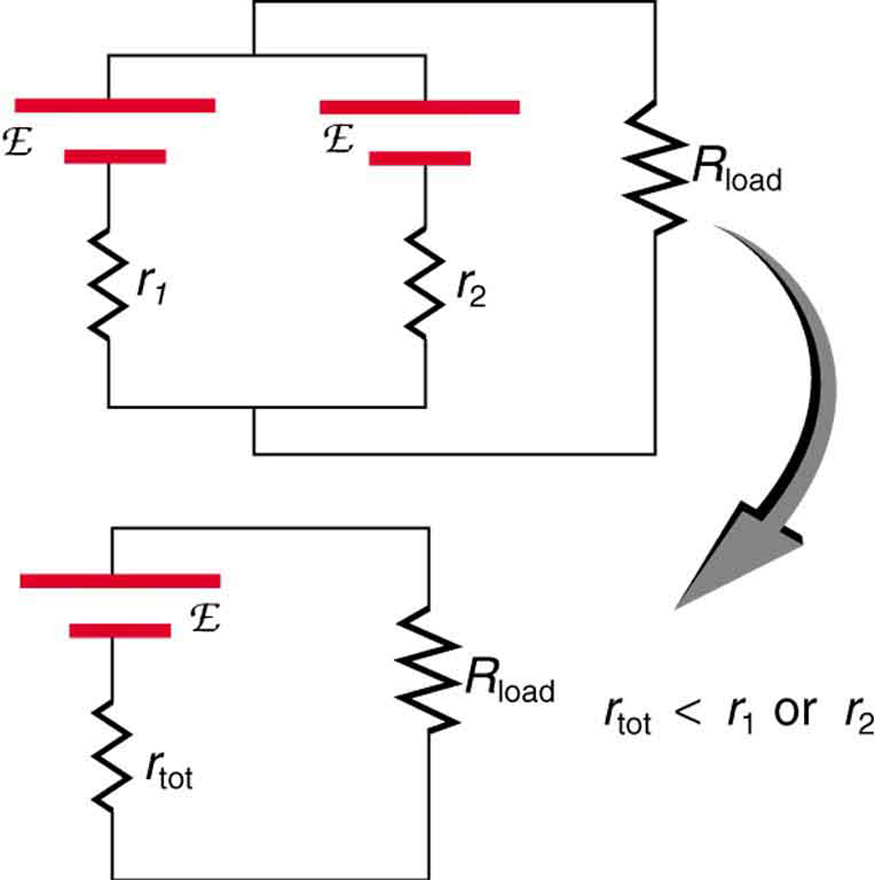
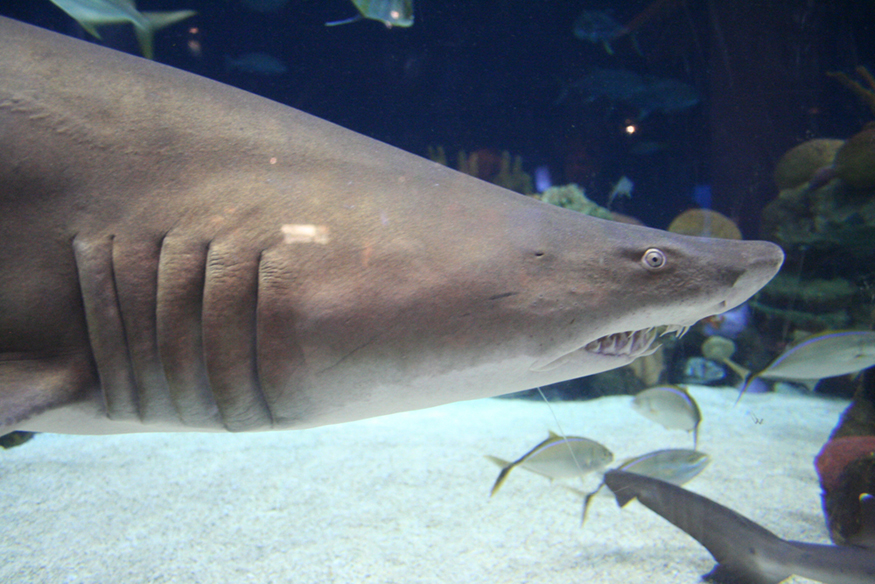
Here, flows through the load, and is less than those of the individual batteries. For example, some diesel-powered cars use two 12-V batteries in parallel; they produce a total emf of 12 V but can deliver the larger current needed to start a diesel engine.
A number of animals both produce and detect electrical signals. Fish, sharks, platypuses, and echidnas (spiny anteaters) all detect electric fields generated by nerve activity in prey. Electric eels produce their own emf through biological cells (electric organs) called electroplaques, which are arranged in both series and parallel as a set of batteries.
Electroplaques are flat, disk-like cells; those of the electric eel have a voltage of 0.15 V across each one. These cells are usually located toward the head or tail of the animal, although in the case of the electric eel, they are found along the entire body. The electroplaques in the South American eel are arranged in 140 rows, with each row stretching horizontally along the body and containing 5,000 electroplaques. This can yield an emf of approximately 600 V, and a current of 1 A—deadly.
The mechanism for detection of external electric fields is similar to that for producing nerve signals in the cell through depolarization and repolarization—the movement of ions across the cell membrane. Within the fish, weak electric fields in the water produce a current in a gel-filled canal that runs from the skin to sensing cells, producing a nerve signal. The Australian platypus, one of the very few mammals that lay eggs, can detect fields of 30 , while sharks have been found to be able to sense a field in their snouts as small as 100 ( [link] ). Electric eels use their own electric fields produced by the electroplaques to stun their prey or enemies.

Another example dealing with multiple voltage sources is that of combinations of solar cells—wired in both series and parallel combinations to yield a desired voltage and current. Photovoltaic generation (PV), the conversion of sunlight directly into electricity, is based upon the photoelectric effect, in which photons hitting the surface of a solar cell create an electric current in the cell.
Most solar cells are made from pure silicon—either as single-crystal silicon, or as a thin film of silicon deposited upon a glass or metal backing. Most single cells have a voltage output of about 0.5 V, while the current output is a function of the amount of sunlight upon the cell (the incident solar radiation—the insolation). Under bright noon sunlight, a current of about of cell surface area is produced by typical single-crystal cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?