| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A non-satellite body fulfilling only the first two of the above criteria is classified as “dwarf planet.”
In 2006, Pluto was demoted to a ‘dwarf planet’ after scientists revised their definition of what constitutes a “true” planet.
| Parent | Satellite | Average orbital radius r (km) | Period T(y) | r 3 / T 2 (km 3 / y 2 ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Earth | Moon | 0.07481 | ||
| Sun | Mercury | 0.2409 | ||
| Venus | 0.6150 | |||
| Earth | 1.000 | |||
| Mars | 1.881 | |||
| Jupiter | 11.86 | |||
| Saturn | 29.46 | |||
| Neptune | 164.8 | |||
| Pluto | 248.3 | |||
| Jupiter | Io | 0.00485 (1.77 d) | ||
| Europa | 0.00972 (3.55 d) | |||
| Ganymede | 0.0196 (7.16 d) | |||
| Callisto | 0.0457 (16.19 d) |
The universal law of gravitation is a good example of a physical principle that is very broadly applicable. That single equation for the gravitational force describes all situations in which gravity acts. It gives a cause for a vast number of effects, such as the orbits of the planets and moons in the solar system. It epitomizes the underlying unity and simplicity of physics.
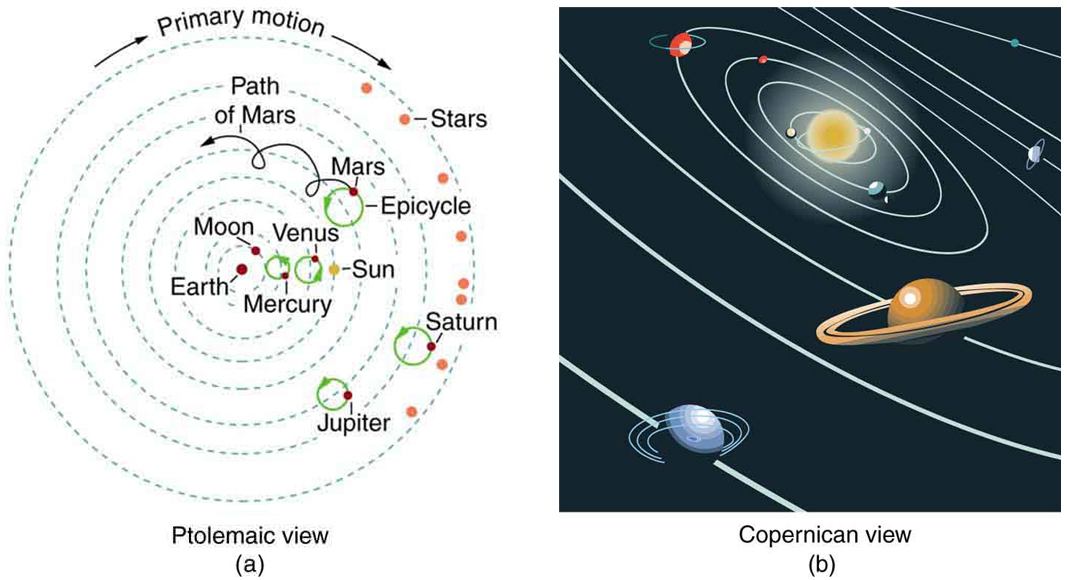
Before the discoveries of Kepler, Copernicus, Galileo, Newton, and others, the solar system was thought to revolve around Earth as shown in [link] (a). This is called the Ptolemaic view, for the Greek philosopher who lived in the second century AD. This model is characterized by a list of facts for the motions of planets with no cause and effect explanation. There tended to be a different rule for each heavenly body and a general lack of simplicity.
[link] (b) represents the modern or Copernican model. In this model, a small set of rules and a single underlying force explain not only all motions in the solar system, but all other situations involving gravity. The breadth and simplicity of the laws of physics are compelling. As our knowledge of nature has grown, the basic simplicity of its laws has become ever more evident.
Kepler’s first law
The orbit of each planet about the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
Kepler’s second law
Each planet moves so that an imaginary line drawn from the Sun to the planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
Kepler’s third law
The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets about the Sun is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average distances from the Sun:
where is the period (time for one orbit) and is the average radius of the orbit.
or

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?