| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
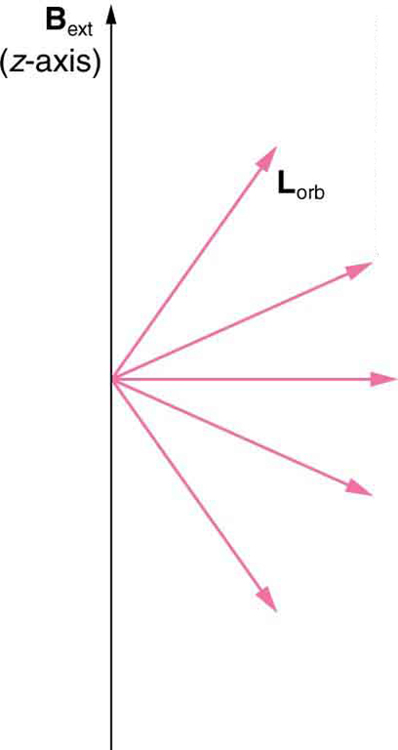
We already know that the magnitude of angular momentum is quantized for electron orbits in atoms. The new insight is that the direction of the orbital angular momentum is also quantized . The fact that the orbital angular momentum can have only certain directions is called space quantization . Like many aspects of quantum mechanics, this quantization of direction is totally unexpected. On the macroscopic scale, orbital angular momentum, such as that of the moon around the earth, can have any magnitude and be in any direction.
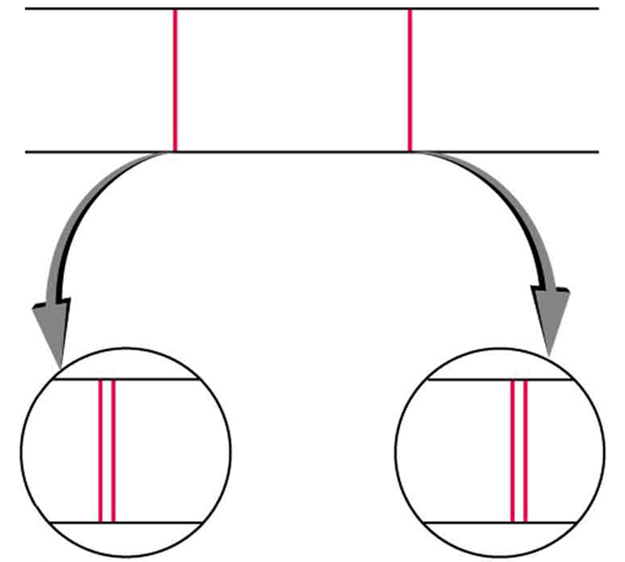
Detailed treatment of space quantization began to explain some complexities of atomic spectra, but certain patterns seemed to be caused by something else. As mentioned, spectral lines are actually closely spaced doublets, a characteristic called fine structure , as shown in [link] . The doublet changes when a magnetic field is applied, implying that whatever causes the doublet interacts with a magnetic field. In 1925, Sem Goudsmit and George Uhlenbeck, two Dutch physicists, successfully argued that electrons have properties analogous to a macroscopic charge spinning on its axis. Electrons, in fact, have an internal or intrinsic angular momentum called intrinsic spin . Since electrons are charged, their intrinsic spin creates an intrinsic magnetic field , which interacts with their orbital magnetic field . Furthermore, electron intrinsic spin is quantized in magnitude and direction , analogous to the situation for orbital angular momentum. The spin of the electron can have only one magnitude, and its direction can be at only one of two angles relative to a magnetic field, as seen in [link] . We refer to this as spin up or spin down for the electron. Each spin direction has a different energy; hence, spectroscopic lines are split into two. Spectral doublets are now understood as being due to electron spin.
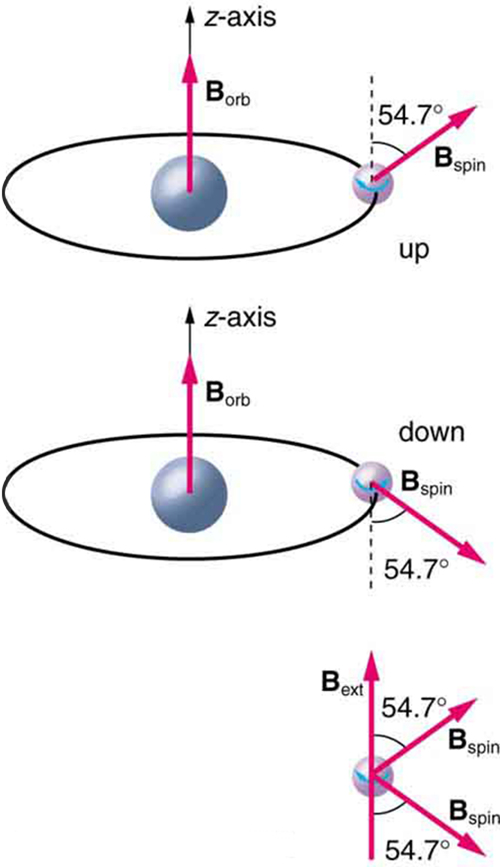
These two new insights—that the direction of angular momentum, whether orbital or spin, is quantized, and that electrons have intrinsic spin—help to explain many of the complexities of atomic and molecular spectra. In magnetic resonance imaging, it is the way that the intrinsic magnetic field of hydrogen and biological atoms interact with an external field that underlies the diagnostic fundamentals.
What is the Zeeman effect, and what type of quantization was discovered because of this effect?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?