| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
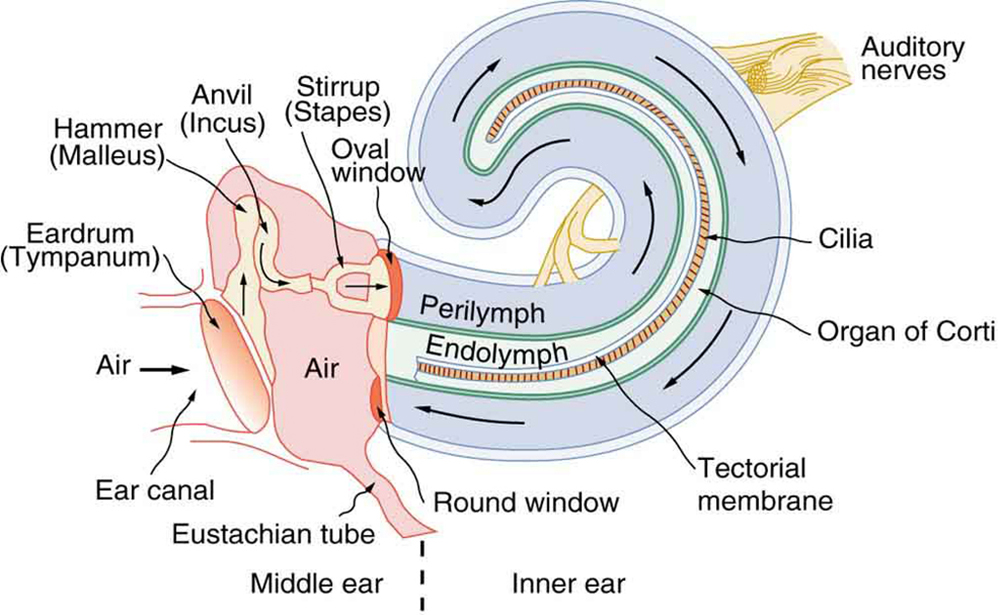
Hearing losses can occur because of problems in the middle or inner ear. Conductive losses in the middle ear can be partially overcome by sending sound vibrations to the cochlea through the skull. Hearing aids for this purpose usually press against the bone behind the ear, rather than simply amplifying the sound sent into the ear canal as many hearing aids do. Damage to the nerves in the cochlea is not repairable, but amplification can partially compensate. There is a risk that amplification will produce further damage. Another common failure in the cochlea is damage or loss of the cilia but with nerves remaining functional. Cochlear implants that stimulate the nerves directly are now available and widely accepted. Over 100,000 implants are in use, in about equal numbers of adults and children.
The cochlear implant was pioneered in Melbourne, Australia, by Graeme Clark in the 1970s for his deaf father. The implant consists of three external components and two internal components. The external components are a microphone for picking up sound and converting it into an electrical signal, a speech processor to select certain frequencies and a transmitter to transfer the signal to the internal components through electromagnetic induction. The internal components consist of a receiver/transmitter secured in the bone beneath the skin, which converts the signals into electric impulses and sends them through an internal cable to the cochlea and an array of about 24 electrodes wound through the cochlea. These electrodes in turn send the impulses directly into the brain. The electrodes basically emulate the cilia.
Are ultrasound and infrasound imperceptible to all hearing organisms? Explain your answer.
No, the range of perceptible sound is based in the range of human hearing. Many other organisms perceive either infrasound or ultrasound.
Why can a hearing test show that your threshold of hearing is 0 dB at 250 Hz, when [link] implies that no one can hear such a frequency at less than 20 dB?
The factor of in the range of intensities to which the ear can respond, from threshold to that causing damage after brief exposure, is truly remarkable. If you could measure distances over the same range with a single instrument and the smallest distance you could measure was 1 mm, what would the largest be?
The frequencies to which the ear responds vary by a factor of . Suppose the speedometer on your car measured speeds differing by the same factor of , and the greatest speed it reads is 90.0 mi/h. What would be the slowest nonzero speed it could read?
What are the closest frequencies to 500 Hz that an average person can clearly distinguish as being different in frequency from 500 Hz? The sounds are not present simultaneously.
498.5 or 501.5 Hz
Can the average person tell that a 2002-Hz sound has a different frequency than a 1999-Hz sound without playing them simultaneously?
If your radio is producing an average sound intensity level of 85 dB, what is the next lowest sound intensity level that is clearly less intense?
82 dB
Can you tell that your roommate turned up the sound on the TV if its average sound intensity level goes from 70 to 73 dB?
Based on the graph in [link] , what is the threshold of hearing in decibels for frequencies of 60, 400, 1000, 4000, and 15,000 Hz? Note that many AC electrical appliances produce 60 Hz, music is commonly 400 Hz, a reference frequency is 1000 Hz, your maximum sensitivity is near 4000 Hz, and many older TVs produce a 15,750 Hz whine.
approximately 48, 9, 0, –7, and 20 dB, respectively
What sound intensity levels must sounds of frequencies 60, 3000, and 8000 Hz have in order to have the same loudness as a 40-dB sound of frequency 1000 Hz (that is, to have a loudness of 40 phons)?
What is the approximate sound intensity level in decibels of a 600-Hz tone if it has a loudness of 20 phons? If it has a loudness of 70 phons?
(a) 23 dB
(b) 70 dB
(a) What are the loudnesses in phons of sounds having frequencies of 200, 1000, 5000, and 10,000 Hz, if they are all at the same 60.0-dB sound intensity level? (b) If they are all at 110 dB? (c) If they are all at 20.0 dB?
Suppose a person has a 50-dB hearing loss at all frequencies. By how many factors of 10 will low-intensity sounds need to be amplified to seem normal to this person? Note that smaller amplification is appropriate for more intense sounds to avoid further hearing damage.
Five factors of 10
If a woman needs an amplification of times the threshold intensity to enable her to hear at all frequencies, what is her overall hearing loss in dB? Note that smaller amplification is appropriate for more intense sounds to avoid further damage to her hearing from levels above 90 dB.
(a) What is the intensity in watts per meter squared of a just barely audible 200-Hz sound? (b) What is the intensity in watts per meter squared of a barely audible 4000-Hz sound?
(a)
(b)
(a) Find the intensity in watts per meter squared of a 60.0-Hz sound having a loudness of 60 phons. (b) Find the intensity in watts per meter squared of a 10,000-Hz sound having a loudness of 60 phons.
A person has a hearing threshold 10 dB above normal at 100 Hz and 50 dB above normal at 4000 Hz. How much more intense must a 100-Hz tone be than a 4000-Hz tone if they are both barely audible to this person?
2.5
A child has a hearing loss of 60 dB near 5000 Hz, due to noise exposure, and normal hearing elsewhere. How much more intense is a 5000-Hz tone than a 400-Hz tone if they are both barely audible to the child?
What is the ratio of intensities of two sounds of identical frequency if the first is just barely discernible as louder to a person than the second?
1.26

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?