| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By now you can probably guess that Polaroid sunglasses cut the glare in reflected light because that light is polarized. You can check this for yourself by holding Polaroid sunglasses in front of you and rotating them while looking at light reflected from water or glass. As you rotate the sunglasses, you will notice the light gets bright and dim, but not completely black. This implies the reflected light is partially polarized and cannot be completely blocked by a polarizing filter.
[link] illustrates what happens when unpolarized light is reflected from a surface. Vertically polarized light is preferentially refracted at the surface, so that the reflected light is left more horizontally polarized . The reasons for this phenomenon are beyond the scope of this text, but a convenient mnemonic for remembering this is to imagine the polarization direction to be like an arrow. Vertical polarization would be like an arrow perpendicular to the surface and would be more likely to stick and not be reflected. Horizontal polarization is like an arrow bouncing on its side and would be more likely to be reflected. Sunglasses with vertical axes would then block more reflected light than unpolarized light from other sources.
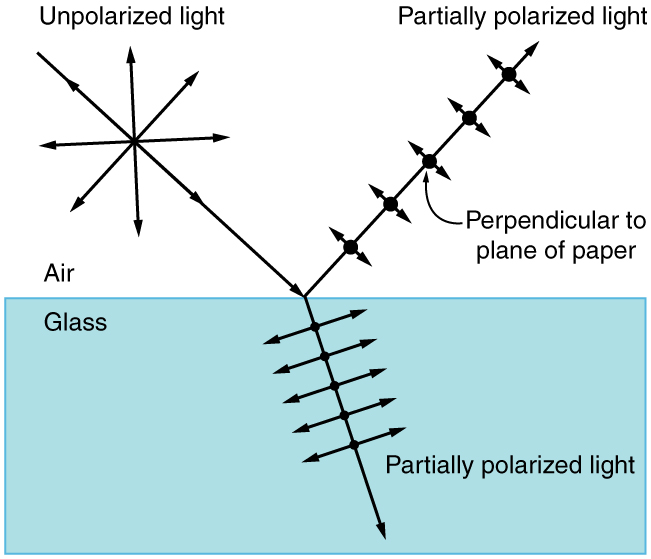
Since the part of the light that is not reflected is refracted, the amount of polarization depends on the indices of refraction of the media involved. It can be shown that reflected light is completely polarized at a angle of reflection , given by
where is the medium in which the incident and reflected light travel and is the index of refraction of the medium that forms the interface that reflects the light. This equation is known as Brewster’s law , and is known as Brewster’s angle , named after the 19th-century Scottish physicist who discovered them.
Polarizing filters have a polarization axis that acts as a slit. This slit passes electromagnetic waves (often visible light) that have an electric field parallel to the axis. This is accomplished with long molecules aligned perpendicular to the axis as shown in [link] .
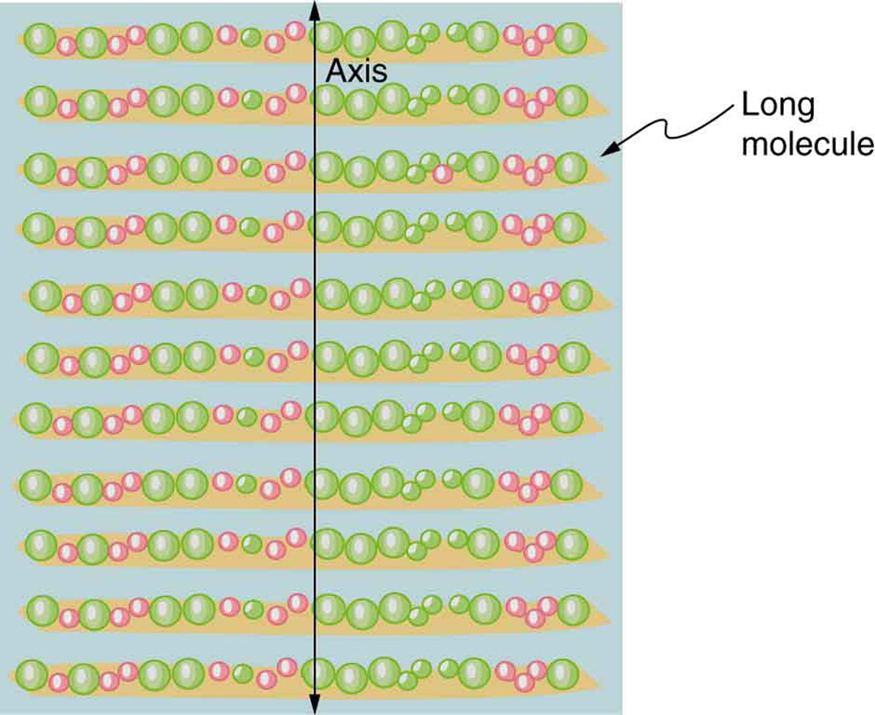
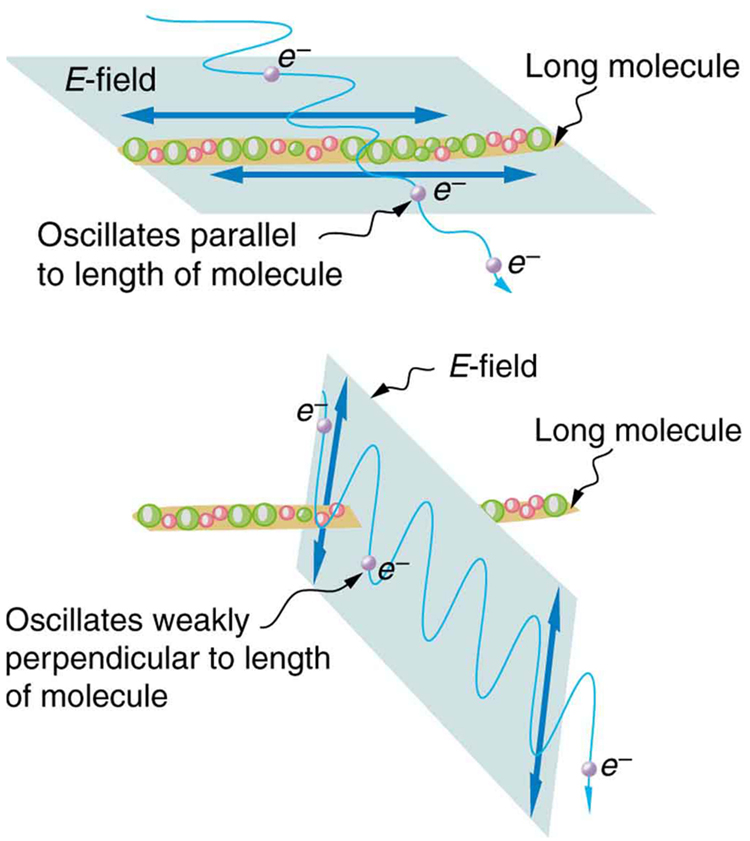
[link] illustrates how the component of the electric field parallel to the long molecules is absorbed. An electromagnetic wave is composed of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The electric field is strong compared with the magnetic field and is more effective in exerting force on charges in the molecules. The most affected charged particles are the electrons in the molecules, since electron masses are small. If the electron is forced to oscillate, it can absorb energy from the EM wave. This reduces the fields in the wave and, hence, reduces its intensity. In long molecules, electrons can more easily oscillate parallel to the molecule than in the perpendicular direction. The electrons are bound to the molecule and are more restricted in their movement perpendicular to the molecule. Thus, the electrons can absorb EM waves that have a component of their electric field parallel to the molecule. The electrons are much less responsive to electric fields perpendicular to the molecule and will allow those fields to pass. Thus the axis of the polarizing filter is perpendicular to the length of the molecule.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?