| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
This equation expresses the two major factors affecting the amount of charge stored. Those factors are the physical characteristics of the capacitor, , and the voltage, . Rearranging the equation, we see that capacitance is the amount of charge stored per volt, or
Capacitance is the amount of charge stored per volt, or
The unit of capacitance is the farad (F), named for Michael Faraday (1791–1867), an English scientist who contributed to the fields of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Since capacitance is charge per unit voltage, we see that a farad is a coulomb per volt, or
A 1-farad capacitor would be able to store 1 coulomb (a very large amount of charge) with the application of only 1 volt. One farad is, thus, a very large capacitance. Typical capacitors range from fractions of a picofarad to millifarads .
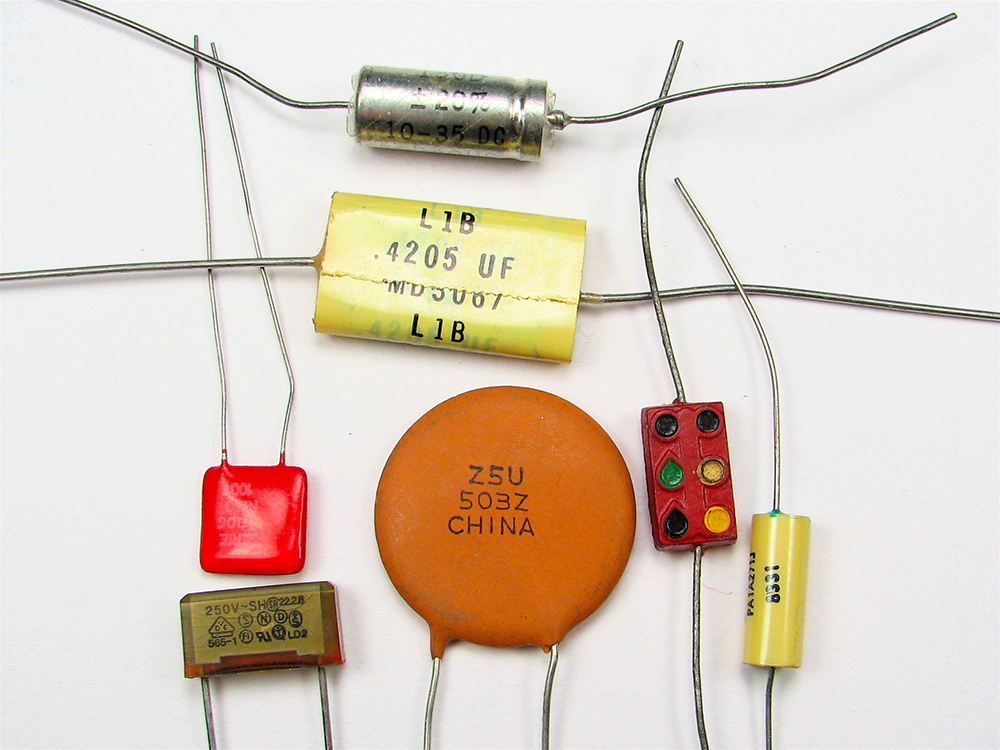
[link] shows some common capacitors. Capacitors are primarily made of ceramic, glass, or plastic, depending upon purpose and size. Insulating materials, called dielectrics, are commonly used in their construction, as discussed below.
The parallel plate capacitor shown in [link] has two identical conducting plates, each having a surface area , separated by a distance (with no material between the plates). When a voltage is applied to the capacitor, it stores a charge , as shown. We can see how its capacitance depends on and by considering the characteristics of the Coulomb force. We know that like charges repel, unlike charges attract, and the force between charges decreases with distance. So it seems quite reasonable that the bigger the plates are, the more charge they can store—because the charges can spread out more. Thus should be greater for larger . Similarly, the closer the plates are together, the greater the attraction of the opposite charges on them. So should be greater for smaller .
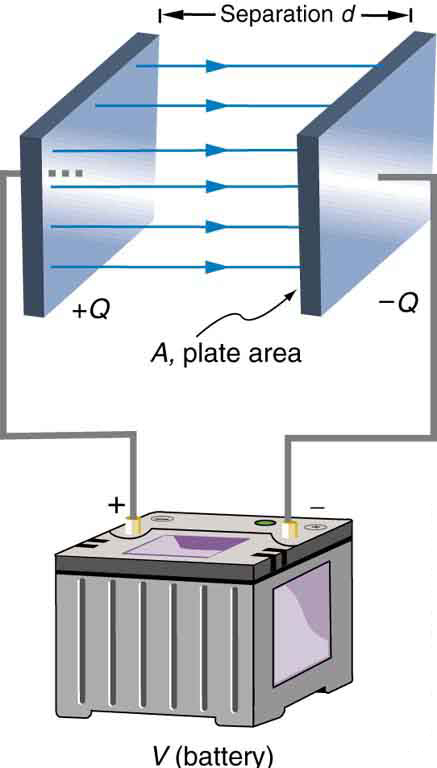
It can be shown that for a parallel plate capacitor there are only two factors ( and ) that affect its capacitance . The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor in equation form is given by
is the area of one plate in square meters, and is the distance between the plates in meters. The constant is the permittivity of free space; its numerical value in SI units is . The units of F/m are equivalent to . The small numerical value of is related to the large size of the farad. A parallel plate capacitor must have a large area to have a capacitance approaching a farad. (Note that the above equation is valid when the parallel plates are separated by air or free space. When another material is placed between the plates, the equation is modified, as discussed below.)
(a) What is the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor with metal plates, each of area , separated by 1.00 mm? (b) What charge is stored in this capacitor if a voltage of is applied to it?
Strategy
Finding the capacitance is a straightforward application of the equation . Once is found, the charge stored can be found using the equation .
Solution for (a)
Entering the given values into the equation for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor yields
Discussion for (a)
This small value for the capacitance indicates how difficult it is to make a device with a large capacitance. Special techniques help, such as using very large area thin foils placed close together.
Solution for (b)
The charge stored in any capacitor is given by the equation . Entering the known values into this equation gives
Discussion for (b)
This charge is only slightly greater than those found in typical static electricity. Since air breaks down at about , more charge cannot be stored on this capacitor by increasing the voltage.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?