| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Because diffusion is typically very slow, its most important effects occur over small distances. For example, the cornea of the eye gets most of its oxygen by diffusion through the thin tear layer covering it.
If you very carefully place a drop of food coloring in a still glass of water, it will slowly diffuse into the colorless surroundings until its concentration is the same everywhere. This type of diffusion is called free diffusion, because there are no barriers inhibiting it. Let us examine its direction and rate. Molecular motion is random in direction, and so simple chance dictates that more molecules will move out of a region of high concentration than into it. The net rate of diffusion is higher initially than after the process is partially completed. (See [link] .)
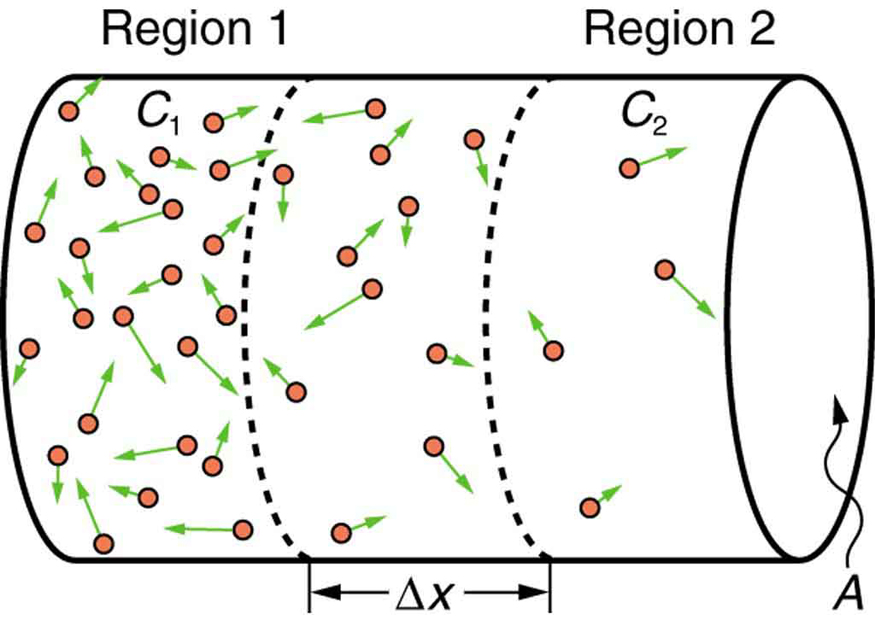
The rate of diffusion is proportional to the concentration difference. Many more molecules will leave a region of high concentration than will enter it from a region of low concentration. In fact, if the concentrations were the same, there would be no net movement. The rate of diffusion is also proportional to the diffusion constant , which is determined experimentally. The farther a molecule can diffuse in a given time, the more likely it is to leave the region of high concentration. Many of the factors that affect the rate are hidden in the diffusion constant . For example, temperature and cohesive and adhesive forces all affect values of .
Diffusion is the dominant mechanism by which the exchange of nutrients and waste products occur between the blood and tissue, and between air and blood in the lungs. In the evolutionary process, as organisms became larger, they needed quicker methods of transportation than net diffusion, because of the larger distances involved in the transport, leading to the development of circulatory systems. Less sophisticated, single-celled organisms still rely totally on diffusion for the removal of waste products and the uptake of nutrients.
Some of the most interesting examples of diffusion occur through barriers that affect the rates of diffusion. For example, when you soak a swollen ankle in Epsom salt, water diffuses through your skin. Many substances regularly move through cell membranes; oxygen moves in, carbon dioxide moves out, nutrients go in, and wastes go out, for example. Because membranes are thin structures (typically to m across) diffusion rates through them can be high. Diffusion through membranes is an important method of transport.
Membranes are generally selectively permeable, or semipermeable . (See [link] .) One type of semipermeable membrane has small pores that allow only small molecules to pass through. In other types of membranes, the molecules may actually dissolve in the membrane or react with molecules in the membrane while moving across. Membrane function, in fact, is the subject of much current research, involving not only physiology but also chemistry and physics.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?