| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
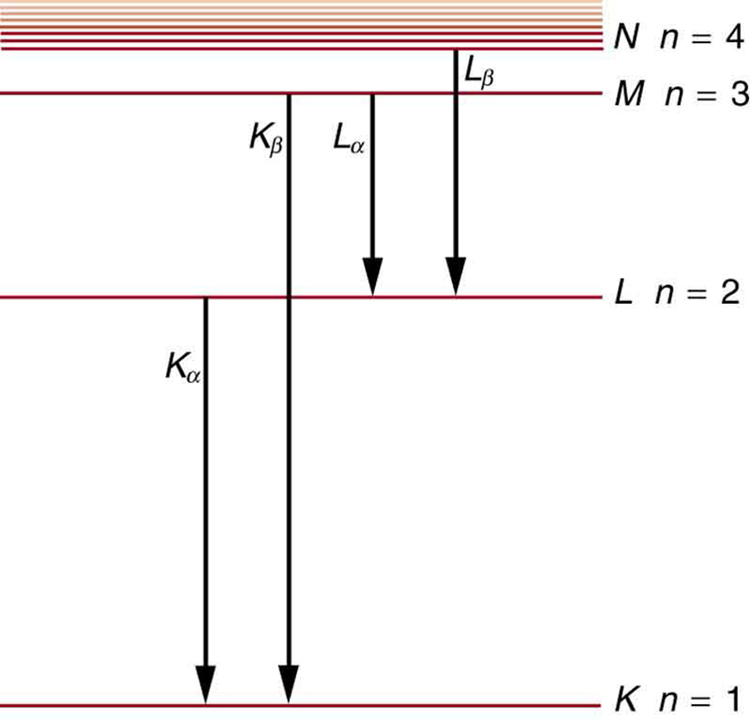
Calculate the approximate energy of a x ray from a tungsten anode in an x-ray tube.
Strategy
How do we calculate energies in a multiple-electron atom? In the case of characteristic x rays, the following approximate calculation is reasonable. Characteristic x rays are produced when an inner-shell vacancy is filled. Inner-shell electrons are nearer the nucleus than others in an atom and thus feel little net effect from the others. This is similar to what happens inside a charged conductor, where its excess charge is distributed over the surface so that it produces no electric field inside. It is reasonable to assume the inner-shell electrons have hydrogen-like energies, as given by . As noted, a x ray is produced by an to transition. Since there are two electrons in a filled shell, a vacancy would leave one electron, so that the effective charge would be rather than . For tungsten, , so that the effective charge is 73.
Solution
gives the orbital energies for hydrogen-like atoms to be , where . As noted, the effective is 73. Now the x-ray energy is given by
where
and
Thus,
Discussion
This large photon energy is typical of characteristic x rays from heavy elements. It is large compared with other atomic emissions because it is produced when an inner-shell vacancy is filled, and inner-shell electrons are tightly bound. Characteristic x ray energies become progressively larger for heavier elements because their energy increases approximately as . Significant accelerating voltage is needed to create these inner-shell vacancies. In the case of tungsten, at least 72.5 kV is needed, because other shells are filled and you cannot simply bump one electron to a higher filled shell. Tungsten is a common anode material in x-ray tubes; so much of the energy of the impinging electrons is absorbed, raising its temperature, that a high-melting-point material like tungsten is required.
All of us can identify diagnostic uses of x-ray photons. Among these are the universal dental and medical x rays that have become an essential part of medical diagnostics. (See [link] and [link] .) X rays are also used to inspect our luggage at airports, as shown in [link] , and for early detection of cracks in crucial aircraft components. An x ray is not only a noun meaning high-energy photon, it also is an image produced by x rays, and it has been made into a familiar verb—to be x-rayed.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?