| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

Have you ever driven on a road that seems like it goes on forever? If you look ahead, you might say you have about 10 km left to go. Another traveler might say the road ahead looks like it’s about 15 km long. If you both measured the road, however, you would agree. Traveling at everyday speeds, the distance you both measure would be the same. You will read in this section, however, that this is not true at relativistic speeds. Close to the speed of light, distances measured are not the same when measured by different observers.
One thing all observers agree upon is relative speed. Even though clocks measure different elapsed times for the same process, they still agree that relative speed, which is distance divided by elapsed time, is the same. This implies that distance, too, depends on the observer’s relative motion. If two observers see different times, then they must also see different distances for relative speed to be the same to each of them.
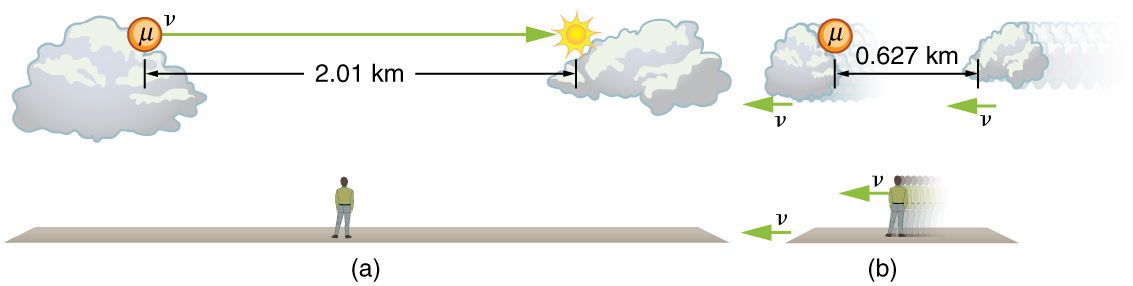
The muon discussed in [link] illustrates this concept. To an observer on the Earth, the muon travels at for from the time it is produced until it decays. Thus it travels a distance
relative to the Earth. In the muon’s frame of reference, its lifetime is only . It has enough time to travel only
The distance between the same two events (production and decay of a muon) depends on who measures it and how they are moving relative to it.
Proper length is the distance between two points measured by an observer who is at rest relative to both of the points.
The Earth-bound observer measures the proper length , because the points at which the muon is produced and decays are stationary relative to the Earth. To the muon, the Earth, air, and clouds are moving, and so the distance it sees is not the proper length.
To develop an equation relating distances measured by different observers, we note that the velocity relative to the Earth-bound observer in our muon example is given by
The time relative to the Earth-bound observer is , since the object being timed is moving relative to this observer. The velocity relative to the moving observer is given by
The moving observer travels with the muon and therefore observes the proper time . The two velocities are identical; thus,
We know that . Substituting this equation into the relationship above gives

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?