| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Solution
1. Identify the knowns. ; ; ; .
2. Choose the kinematic equation that makes it easiest to solve the problem. The equation works well because the only unknown in it is . (We will plug in for .)
3. Enter the known values
where we have retained extra significant figures because this is an intermediate result.
Taking the square root, and noting that a square root can be positive or negative, gives
The negative root is chosen to indicate that the rock is still heading down. Thus,
Discussion
Note that this is exactly the same velocity the rock had at this position when it was thrown straight upward with the same initial speed . (See [link] and [link] (a).) This is not a coincidental result. Because we only consider the acceleration due to gravity in this problem, the speed of a falling object depends only on its initial speed and its vertical position relative to the starting point. For example, if the velocity of the rock is calculated at a height of 8.10 m above the starting point (using the method from [link] ) when the initial velocity is 13.0 m/s straight up, a result of is obtained. Here both signs are meaningful; the positive value occurs when the rock is at 8.10 m and heading up, and the negative value occurs when the rock is at 8.10 m and heading back down. It has the same speed but the opposite direction.
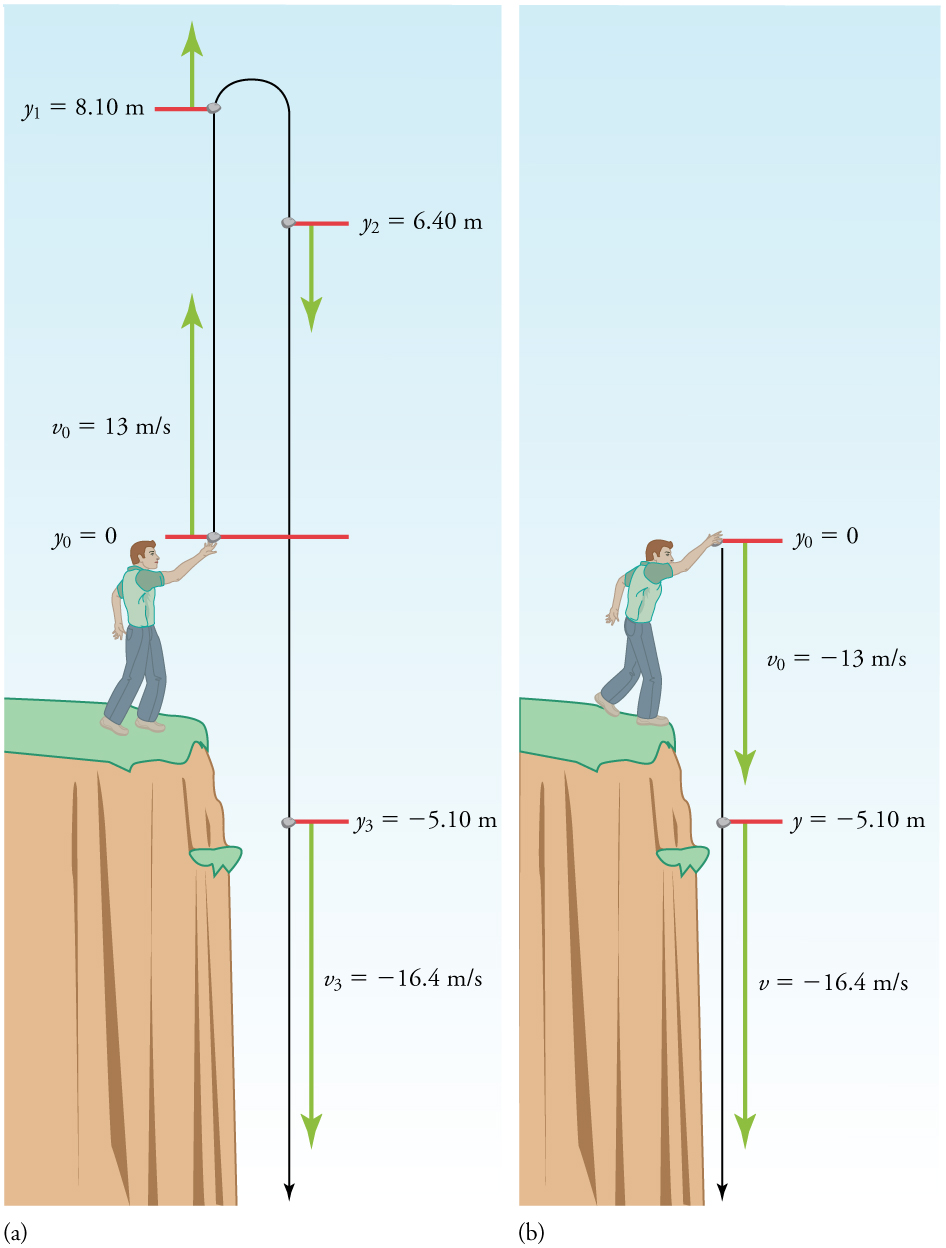
Another way to look at it is this: In [link] , the rock is thrown up with an initial velocity of . It rises and then falls back down. When its position is on its way back down, its velocity is . That is, it has the same speed on its way down as on its way up. We would then expect its velocity at a position of to be the same whether we have thrown it upwards at or thrown it downwards at . The velocity of the rock on its way down from is the same whether we have thrown it up or down to start with, as long as the speed with which it was initially thrown is the same.
The acceleration due to gravity on Earth differs slightly from place to place, depending on topography (e.g., whether you are on a hill or in a valley) and subsurface geology (whether there is dense rock like iron ore as opposed to light rock like salt beneath you.) The precise acceleration due to gravity can be calculated from data taken in an introductory physics laboratory course. An object, usually a metal ball for which air resistance is negligible, is dropped and the time it takes to fall a known distance is measured. See, for example, [link] . Very precise results can be produced with this method if sufficient care is taken in measuring the distance fallen and the elapsed time.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?