| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
where is Planck’s constant and is the photon wavelength. (Note that relativistic momentum given as is valid only for particles having mass.)
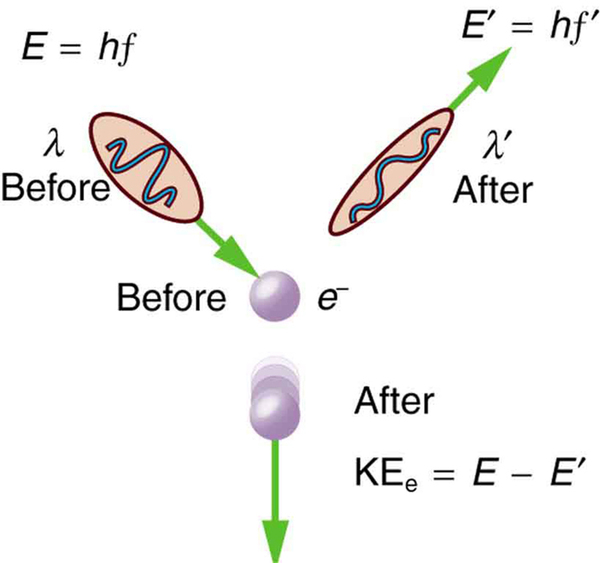
We can see that photon momentum is small, since and is very small. It is for this reason that we do not ordinarily observe photon momentum. Our mirrors do not recoil when light reflects from them (except perhaps in cartoons). Compton saw the effects of photon momentum because he was observing x rays, which have a small wavelength and a relatively large momentum, interacting with the lightest of particles, the electron.
(a) Calculate the momentum of a visible photon that has a wavelength of 500 nm. (b) Find the velocity of an electron having the same momentum. (c) What is the energy of the electron, and how does it compare with the energy of the photon?
Strategy
Finding the photon momentum is a straightforward application of its definition: . If we find the photon momentum is small, then we can assume that an electron with the same momentum will be nonrelativistic, making it easy to find its velocity and kinetic energy from the classical formulas.
Solution for (a)
Photon momentum is given by the equation:
Entering the given photon wavelength yields
Solution for (b)
Since this momentum is indeed small, we will use the classical expression to find the velocity of an electron with this momentum. Solving for and using the known value for the mass of an electron gives
Solution for (c)
The electron has kinetic energy, which is classically given by
Thus,
Converting this to eV by multiplying by yields
The photon energy is
which is about five orders of magnitude greater.
Discussion
Photon momentum is indeed small. Even if we have huge numbers of them, the total momentum they carry is small. An electron with the same momentum has a 1460 m/s velocity, which is clearly nonrelativistic. A more massive particle with the same momentum would have an even smaller velocity. This is borne out by the fact that it takes far less energy to give an electron the same momentum as a photon. But on a quantum-mechanical scale, especially for high-energy photons interacting with small masses, photon momentum is significant. Even on a large scale, photon momentum can have an effect if there are enough of them and if there is nothing to prevent the slow recoil of matter. Comet tails are one example, but there are also proposals to build space sails that use huge low-mass mirrors (made of aluminized Mylar) to reflect sunlight. In the vacuum of space, the mirrors would gradually recoil and could actually take spacecraft from place to place in the solar system. (See [link] .)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?