| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Entering known values into this equation gives
Thus,
Discussion
It is instructive to calculate the internal kinetic energy of this two-object system before and after the collision. (This calculation is left as an end-of-chapter problem.) If you do this calculation, you will find that the internal kinetic energy is less after the collision, and so the collision is inelastic. This type of result makes a physicist want to explore the system further.
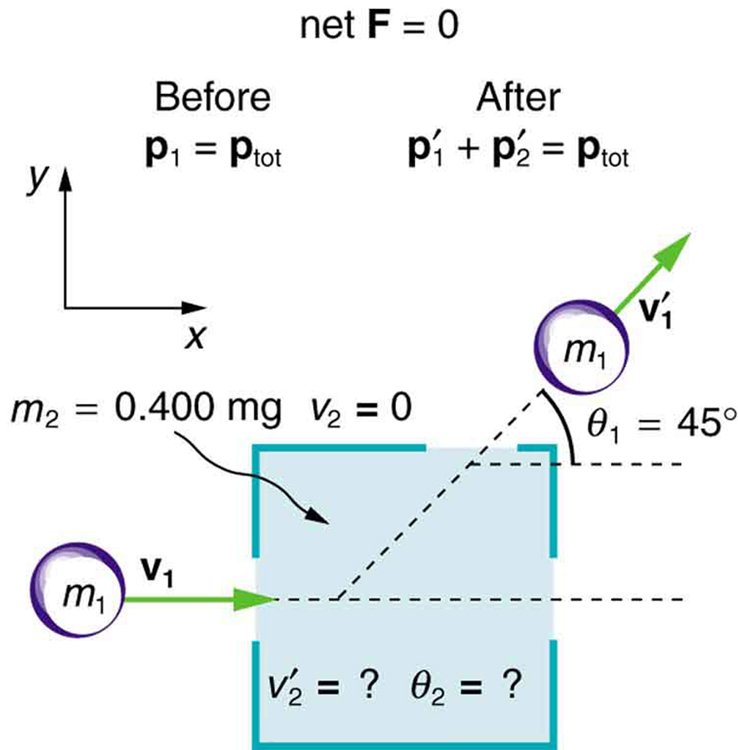
Some interesting situations arise when the two colliding objects have equal mass and the collision is elastic. This situation is nearly the case with colliding billiard balls, and precisely the case with some subatomic particle collisions. We can thus get a mental image of a collision of subatomic particles by thinking about billiards (or pool). (Refer to [link] for masses and angles.) First, an elastic collision conserves internal kinetic energy. Again, let us assume object 2 is initially at rest. Then, the internal kinetic energy before and after the collision of two objects that have equal masses is
Because the masses are equal, . Algebraic manipulation (left to the reader) of conservation of momentum in the - and -directions can show that
(Remember that is negative here.) The two preceding equations can both be true only if
There are three ways that this term can be zero. They are
All three of these ways are familiar occurrences in billiards and pool, although most of us try to avoid the second. If you play enough pool, you will notice that the angle between the balls is very close to after the collision, although it will vary from this value if a great deal of spin is placed on the ball. (Large spin carries in extra energy and a quantity called angular momentum , which must also be conserved.) The assumption that the scattering of billiard balls is elastic is reasonable based on the correctness of the three results it produces. This assumption also implies that, to a good approximation, momentum is conserved for the two-ball system in billiards and pool. The problems below explore these and other characteristics of two-dimensional collisions.
Two-dimensional collision experiments have revealed much of what we know about subatomic particles, as we shall see in Medical Applications of Nuclear Physics and Particle Physics . Ernest Rutherford, for example, discovered the nature of the atomic nucleus from such experiments.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?