| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

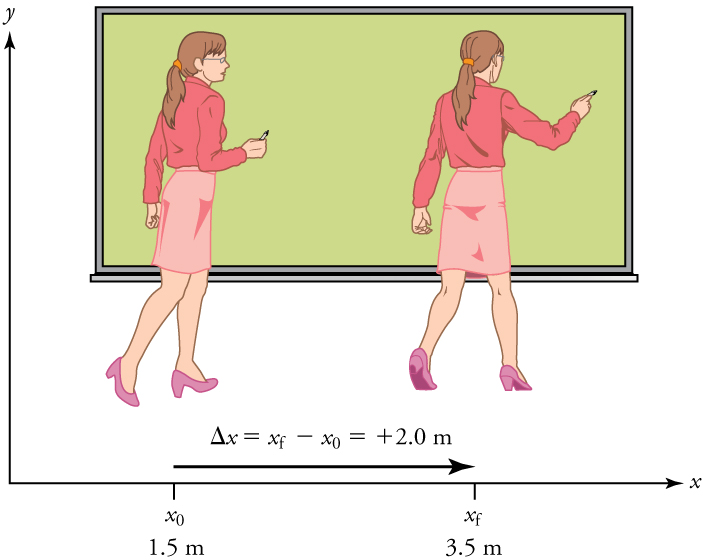
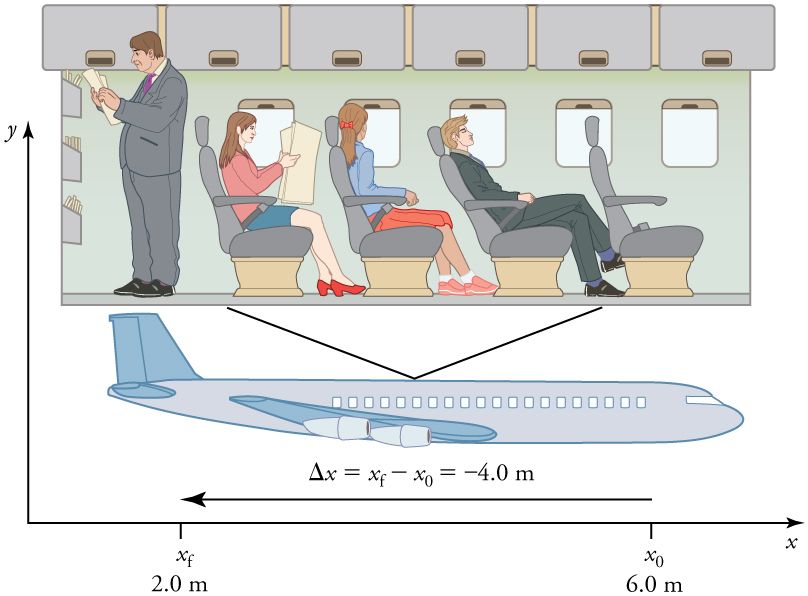
In order to describe the motion of an object, you must first be able to describe its position —where it is at any particular time. More precisely, you need to specify its position relative to a convenient reference frame. Earth is often used as a reference frame, and we often describe the position of an object as it relates to stationary objects in that reference frame. For example, a rocket launch would be described in terms of the position of the rocket with respect to the Earth as a whole, while a professor’s position could be described in terms of where she is in relation to the nearby white board. (See [link] .) In other cases, we use reference frames that are not stationary but are in motion relative to the Earth. To describe the position of a person in an airplane, for example, we use the airplane, not the Earth, as the reference frame. (See [link] .)
If an object moves relative to a reference frame (for example, if a professor moves to the right relative to a white board or a passenger moves toward the rear of an airplane), then the object’s position changes. This change in position is known as displacement . The word “displacement” implies that an object has moved, or has been displaced.
Displacement is the change in position of an object:
where is displacement, is the final position, and is the initial position.
In this text the upper case Greek letter (delta) always means “change in” whatever quantity follows it; thus, means change in position . Always solve for displacement by subtracting initial position from final position .
Note that the SI unit for displacement is the meter (m) (see Physical Quantities and Units ), but sometimes kilometers, miles, feet, and other units of length are used. Keep in mind that when units other than the meter are used in a problem, you may need to convert them into meters to complete the calculation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?