| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Kepler’s Third Law
The ratio of the squares of the periods of any two planets about the Sun is equal to the ratio of the cubes of their average distances from the Sun. In equation form, this is
where is the period (time for one orbit) and is the average radius. This equation is valid only for comparing two small masses orbiting the same large one. Most importantly, this is a descriptive equation only, giving no information as to the cause of the equality.
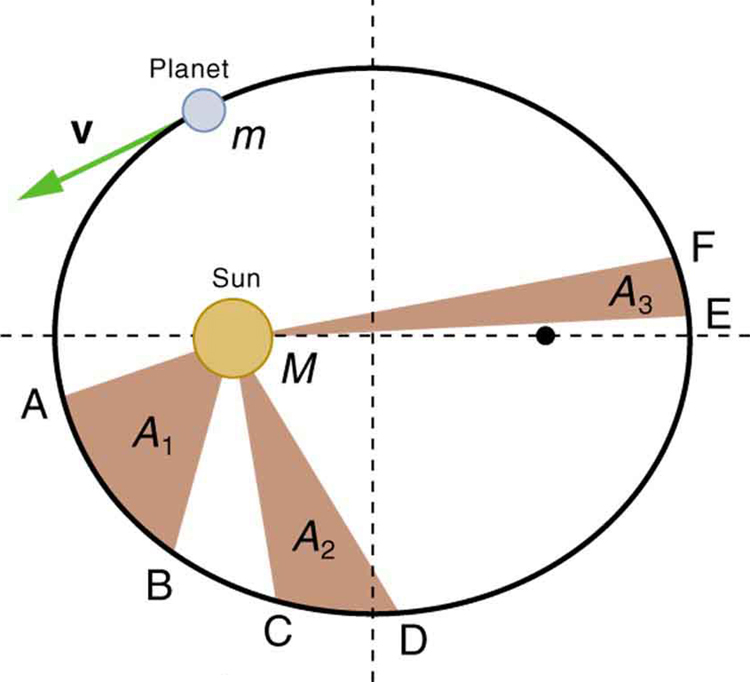
Note again that while, for historical reasons, Kepler’s laws are stated for planets orbiting the Sun, they are actually valid for all bodies satisfying the two previously stated conditions.
Given that the Moon orbits Earth each 27.3 d and that it is an average distance of from the center of Earth, calculate the period of an artificial satellite orbiting at an average altitude of 1500 km above Earth’s surface.
Strategy
The period, or time for one orbit, is related to the radius of the orbit by Kepler’s third law, given in mathematical form in . Let us use the subscript 1 for the Moon and the subscript 2 for the satellite. We are asked to find . The given information tells us that the orbital radius of the Moon is , and that the period of the Moon is . The height of the artificial satellite above Earth’s surface is given, and so we must add the radius of Earth (6380 km) to get . Now all quantities are known, and so can be found.
Solution
Kepler’s third law is
To solve for , we cross-multiply and take the square root, yielding
Substituting known values yields
Discussion This is a reasonable period for a satellite in a fairly low orbit. It is interesting that any satellite at this altitude will orbit in the same amount of time. This fact is related to the condition that the satellite’s mass is small compared with that of Earth.
People immediately search for deeper meaning when broadly applicable laws, like Kepler’s, are discovered. It was Newton who took the next giant step when he proposed the law of universal gravitation. While Kepler was able to discover what was happening, Newton discovered that gravitational force was the cause.
We shall derive Kepler’s third law, starting with Newton’s laws of motion and his universal law of gravitation. The point is to demonstrate that the force of gravity is the cause for Kepler’s laws (although we will only derive the third one).
Let us consider a circular orbit of a small mass around a large mass , satisfying the two conditions stated at the beginning of this section. Gravity supplies the centripetal force to mass . Starting with Newton’s second law applied to circular motion,

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?