| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Thus, to obtain destructive interference for a single slit ,
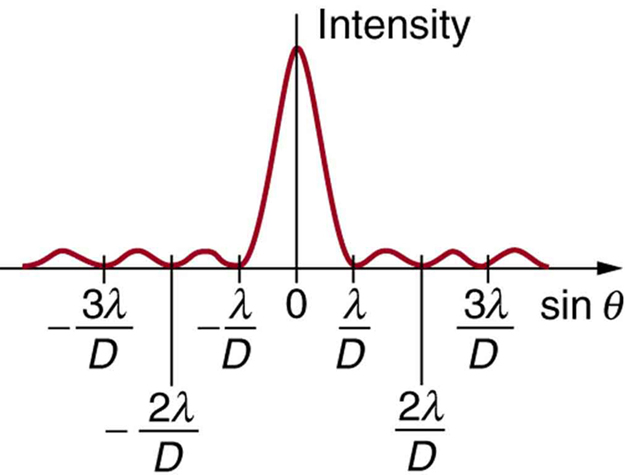
where is the slit width, is the light’s wavelength, is the angle relative to the original direction of the light, and is the order of the minimum. [link] shows a graph of intensity for single slit interference, and it is apparent that the maxima on either side of the central maximum are much less intense and not as wide. This is consistent with the illustration in [link] (b).
Visible light of wavelength 550 nm falls on a single slit and produces its second diffraction minimum at an angle of relative to the incident direction of the light. (a) What is the width of the slit? (b) At what angle is the first minimum produced?
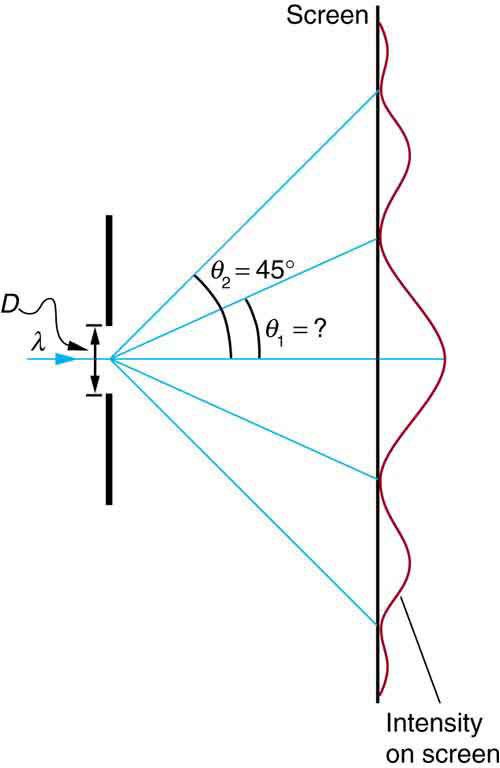
Strategy
From the given information, and assuming the screen is far away from the slit, we can use the equation first to find , and again to find the angle for the first minimum .
Solution for (a)
We are given that , , and . Solving the equation for and substituting known values gives
Solution for (b)
Solving the equation for and substituting the known values gives
Thus the angle is
Discussion
We see that the slit is narrow (it is only a few times greater than the wavelength of light). This is consistent with the fact that light must interact with an object comparable in size to its wavelength in order to exhibit significant wave effects such as this single slit diffraction pattern. We also see that the central maximum extends on either side of the original beam, for a width of about . The angle between the first and second minima is only about . Thus the second maximum is only about half as wide as the central maximum.
As the width of the slit producing a single-slit diffraction pattern is reduced, how will the diffraction pattern produced change?
(a) At what angle is the first minimum for 550-nm light falling on a single slit of width ? (b) Will there be a second minimum?
(a)
(b) No
(a) Calculate the angle at which a -wide slit produces its first minimum for 410-nm violet light. (b) Where is the first minimum for 700-nm red light?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?