| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Strategy
Since temperatures are given for the hot and cold reservoirs of this heat engine, can be used to calculate the Carnot (maximum theoretical) efficiency. Those temperatures must first be converted to kelvins.
Solution
The hot and cold reservoir temperatures are given as and , respectively. In kelvins, then, and , so that the maximum efficiency is
Thus,
Discussion
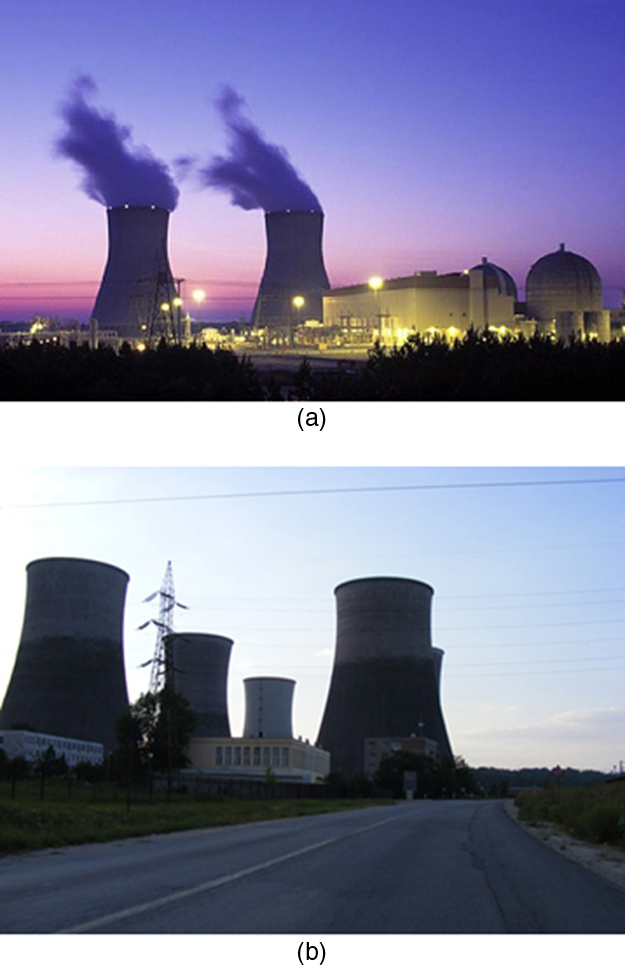
A typical nuclear power station’s actual efficiency is about 35%, a little better than 0.7 times the maximum possible value, a tribute to superior engineering. Electrical power stations fired by coal, oil, and natural gas have greater actual efficiencies (about 42%), because their boilers can reach higher temperatures and pressures. The cold reservoir temperature in any of these power stations is limited by the local environment. [link] shows (a) the exterior of a nuclear power station and (b) the exterior of a coal-fired power station. Both have cooling towers into which water from the condenser enters the tower near the top and is sprayed downward, cooled by evaporation.

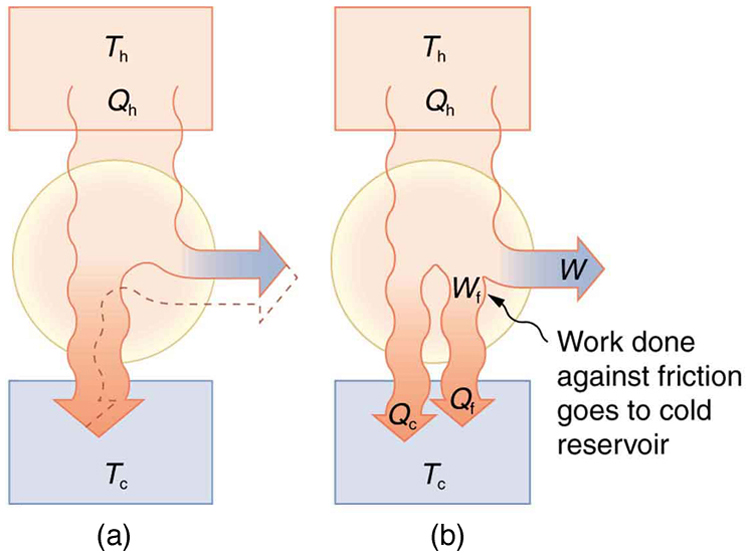
Since all real processes are irreversible, the actual efficiency of a heat engine can never be as great as that of a Carnot engine, as illustrated in [link] (a). Even with the best heat engine possible, there are always dissipative processes in peripheral equipment, such as electrical transformers or car transmissions. These further reduce the overall efficiency by converting some of the engine’s work output back into heat transfer, as shown in [link] (b).
Think about the drinking bird at the beginning of this section ( [link] ). Although the bird enjoys the theoretical maximum efficiency possible, if left to its own devices over time, the bird will cease “drinking.” What are some of the dissipative processes that might cause the bird’s motion to cease?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?