| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Solution for Remaining Times
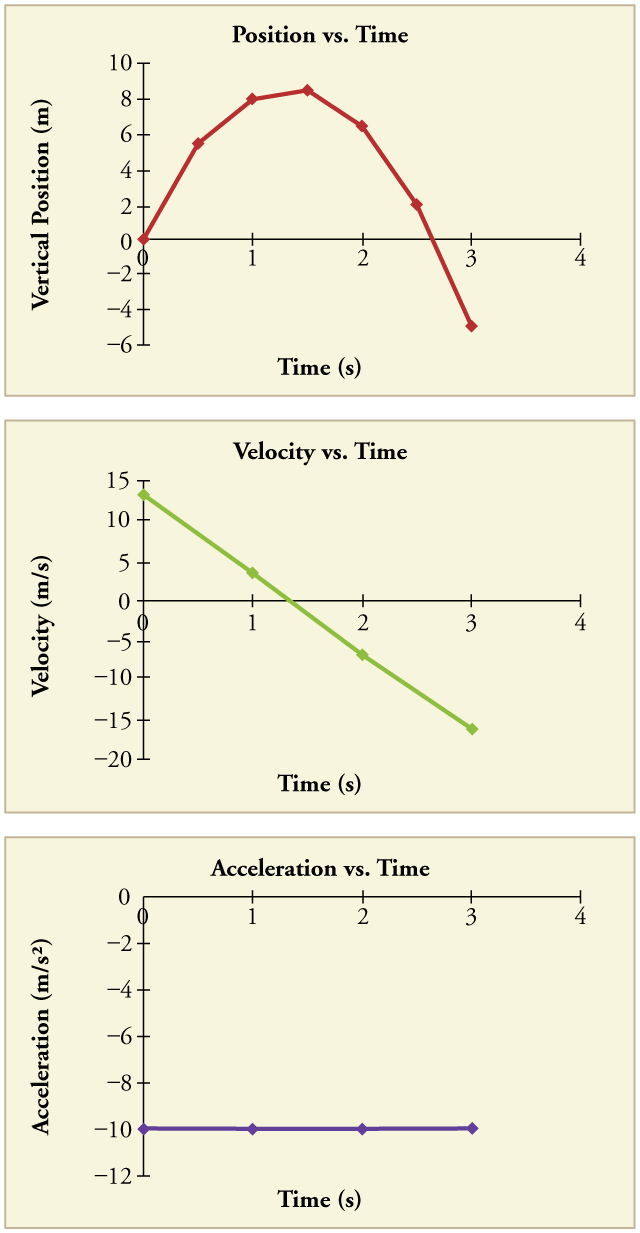
The procedures for calculating the position and velocity at and are the same as those above. The results are summarized in [link] and illustrated in [link] .
| Time, t | Position, y | Velocity, v | Acceleration, a |
|---|---|---|---|
Graphing the data helps us understand it more clearly.
Discussion
The interpretation of these results is important. At 1.00 s the rock is above its starting point and heading upward, since and are both positive. At 2.00 s, the rock is still above its starting point, but the negative velocity means it is moving downward. At 3.00 s, both and are negative, meaning the rock is below its starting point and continuing to move downward. Notice that when the rock is at its highest point (at 1.5 s), its velocity is zero, but its acceleration is still . Its acceleration is for the whole trip—while it is moving up and while it is moving down. Note that the values for are the positions (or displacements) of the rock, not the total distances traveled. Finally, note that free-fall applies to upward motion as well as downward. Both have the same acceleration—the acceleration due to gravity, which remains constant the entire time. Astronauts training in the famous Vomit Comet, for example, experience free-fall while arcing up as well as down, as we will discuss in more detail later.
A simple experiment can be done to determine your reaction time. Have a friend hold a ruler between your thumb and index finger, separated by about 1 cm. Note the mark on the ruler that is right between your fingers. Have your friend drop the ruler unexpectedly, and try to catch it between your two fingers. Note the new reading on the ruler. Assuming acceleration is that due to gravity, calculate your reaction time. How far would you travel in a car (moving at 30 m/s) if the time it took your foot to go from the gas pedal to the brake was twice this reaction time?
What happens if the person on the cliff throws the rock straight down, instead of straight up? To explore this question, calculate the velocity of the rock when it is 5.10 m below the starting point, and has been thrown downward with an initial speed of 13.0 m/s.
Strategy
Draw a sketch.
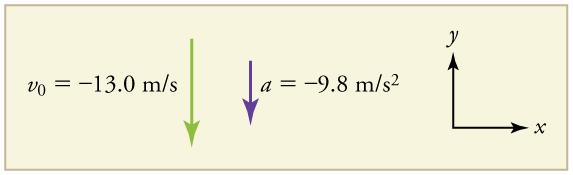
Since up is positive, the final position of the rock will be negative because it finishes below the starting point at . Similarly, the initial velocity is downward and therefore negative, as is the acceleration due to gravity. We expect the final velocity to be negative since the rock will continue to move downward.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?