| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
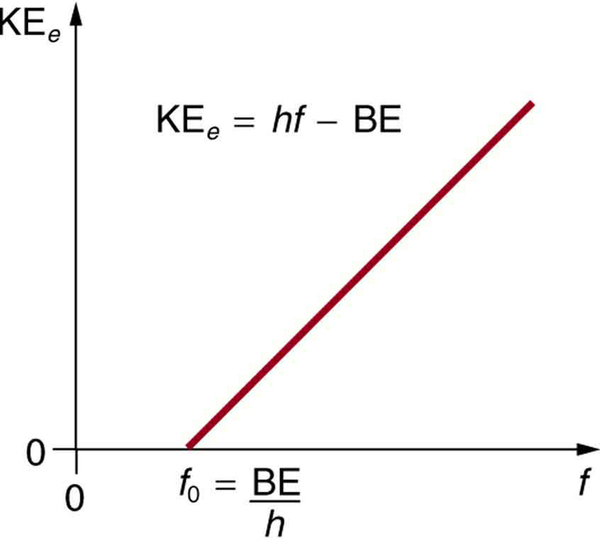
Einstein’s idea that EM radiation is quantized was crucial to the beginnings of quantum mechanics. It is a far more general concept than its explanation of the photoelectric effect might imply. All EM radiation can also be modeled in the form of photons, and the characteristics of EM radiation are entirely consistent with this fact. (As we will see in the next section, many aspects of EM radiation, such as the hazards of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, can be explained only by photon properties.) More famous for modern relativity, Einstein planted an important seed for quantum mechanics in 1905, the same year he published his first paper on special relativity. His explanation of the photoelectric effect was the basis for the Nobel Prize awarded to him in 1921. Although his other contributions to theoretical physics were also noted in that award, special and general relativity were not fully recognized in spite of having been partially verified by experiment by 1921. Although hero-worshipped, this great man never received Nobel recognition for his most famous work—relativity.
(a) What is the energy in joules and electron volts of a photon of 420-nm violet light? (b) What is the maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected from calcium by 420-nm violet light, given that the binding energy (or work function) of electrons for calcium metal is 2.71 eV?
Strategy
To solve part (a), note that the energy of a photon is given by . For part (b), once the energy of the photon is calculated, it is a straightforward application of to find the ejected electron’s maximum kinetic energy, since BE is given.
Solution for (a)
Photon energy is given by
Since we are given the wavelength rather than the frequency, we solve the familiar relationship for the frequency, yielding
Combining these two equations gives the useful relationship
Now substituting known values yields
Converting to eV, the energy of the photon is
Solution for (b)
Finding the kinetic energy of the ejected electron is now a simple application of the equation . Substituting the photon energy and binding energy yields
Discussion
The energy of this 420-nm photon of violet light is a tiny fraction of a joule, and so it is no wonder that a single photon would be difficult for us to sense directly—humans are more attuned to energies on the order of joules. But looking at the energy in electron volts, we can see that this photon has enough energy to affect atoms and molecules. A DNA molecule can be broken with about 1 eV of energy, for example, and typical atomic and molecular energies are on the order of eV, so that the UV photon in this example could have biological effects. The ejected electron (called a photoelectron ) has a rather low energy, and it would not travel far, except in a vacuum. The electron would be stopped by a retarding potential of but 0.26 eV. In fact, if the photon wavelength were longer and its energy less than 2.71 eV, then the formula would give a negative kinetic energy, an impossibility. This simply means that the 420-nm photons with their 2.96-eV energy are not much above the frequency threshold. You can show for yourself that the threshold wavelength is 459 nm (blue light). This means that if calcium metal is used in a light meter, the meter will be insensitive to wavelengths longer than those of blue light. Such a light meter would be completely insensitive to red light, for example.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?