| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
where is the wavelength of light (or other electromagnetic radiation) and is the diameter of the aperture, lens, mirror, etc., with which the two objects are observed. In this expression, has units of radians.
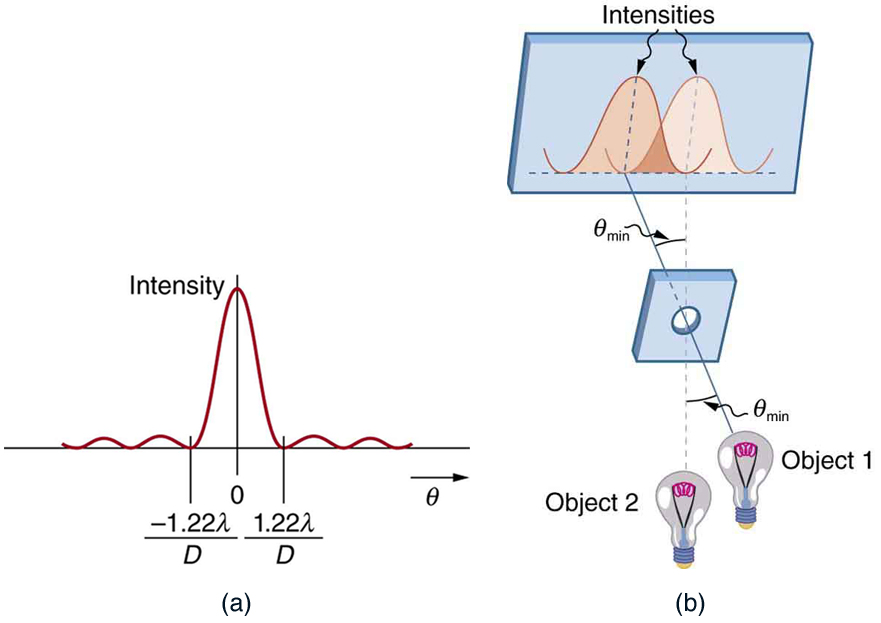
All attempts to observe the size and shape of objects are limited by the wavelength of the probe. Even the small wavelength of light prohibits exact precision. When extremely small wavelength probes as with an electron microscope are used, the system is disturbed, still limiting our knowledge, much as making an electrical measurement alters a circuit. Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle asserts that this limit is fundamental and inescapable, as we shall see in quantum mechanics.
The primary mirror of the orbiting Hubble Space Telescope has a diameter of 2.40 m. Being in orbit, this telescope avoids the degrading effects of atmospheric distortion on its resolution. (a) What is the angle between two just-resolvable point light sources (perhaps two stars)? Assume an average light wavelength of 550 nm. (b) If these two stars are at the 2 million light year distance of the Andromeda galaxy, how close together can they be and still be resolved? (A light year, or ly, is the distance light travels in 1 year.)
Strategy
The Rayleigh criterion stated in the equation gives the smallest possible angle between point sources, or the best obtainable resolution. Once this angle is found, the distance between stars can be calculated, since we are given how far away they are.
Solution for (a)
The Rayleigh criterion for the minimum resolvable angle is
Entering known values gives
Solution for (b)
The distance between two objects a distance away and separated by an angle is .
Substituting known values gives
Discussion
The angle found in part (a) is extraordinarily small (less than 1/50,000 of a degree), because the primary mirror is so large compared with the wavelength of light. As noticed, diffraction effects are most noticeable when light interacts with objects having sizes on the order of the wavelength of light. However, the effect is still there, and there is a diffraction limit to what is observable. The actual resolution of the Hubble Telescope is not quite as good as that found here. As with all instruments, there are other effects, such as non-uniformities in mirrors or aberrations in lenses that further limit resolution. However, [link] gives an indication of the extent of the detail observable with the Hubble because of its size and quality and especially because it is above the Earth’s atmosphere.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?