| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
so that
where is the total work done by all nonconservative forces and is the total work done by all conservative forces.
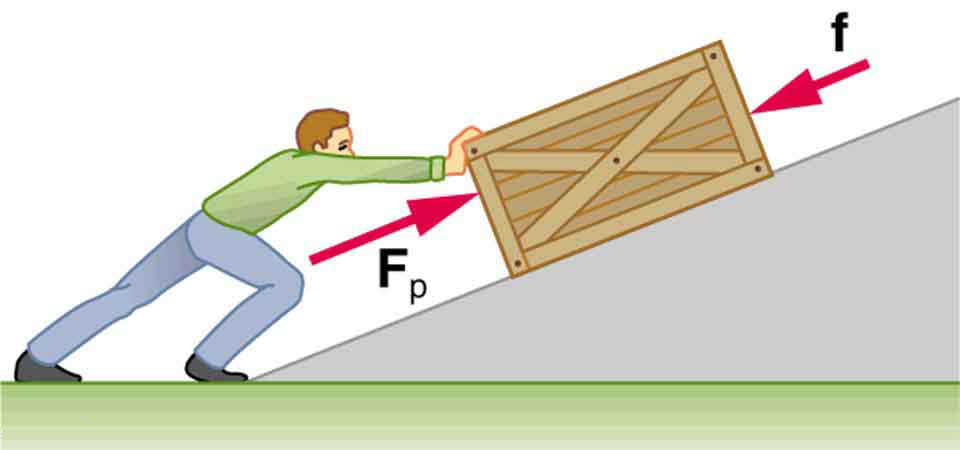
Consider [link] , in which a person pushes a crate up a ramp and is opposed by friction. As in the previous section, we note that work done by a conservative force comes from a loss of gravitational potential energy, so that . Substituting this equation into the previous one and solving for gives
This equation means that the total mechanical energy changes by exactly the amount of work done by nonconservative forces. In [link] , this is the work done by the person minus the work done by friction. So even if energy is not conserved for the system of interest (such as the crate), we know that an equal amount of work was done to cause the change in total mechanical energy.
We rearrange to obtain
This means that the amount of work done by nonconservative forces adds to the mechanical energy of a system. If is positive, then mechanical energy is increased, such as when the person pushes the crate up the ramp in [link] . If is negative, then mechanical energy is decreased, such as when the rock hits the ground in [link] (b). If is zero, then mechanical energy is conserved, and nonconservative forces are balanced. For example, when you push a lawn mower at constant speed on level ground, your work done is removed by the work of friction, and the mower has a constant energy.
When no change in potential energy occurs, applying amounts to applying the work-energy theorem by setting the change in kinetic energy to be equal to the net work done on the system, which in the most general case includes both conservative and nonconservative forces. But when seeking instead to find a change in total mechanical energy in situations that involve changes in both potential and kinetic energy, the previous equation says that you can start by finding the change in mechanical energy that would have resulted from just the conservative forces, including the potential energy changes, and add to it the work done, with the proper sign, by any nonconservative forces involved.
Consider the situation shown in [link] , where a baseball player slides to a stop on level ground. Using energy considerations, calculate the distance the 65.0-kg baseball player slides, given that his initial speed is 6.00 m/s and the force of friction against him is a constant 450 N.
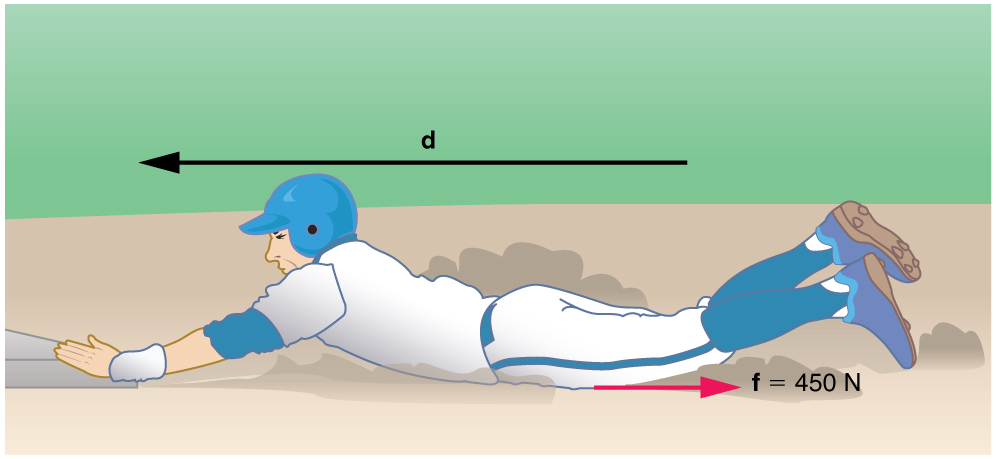
Strategy
Friction stops the player by converting his kinetic energy into other forms, including thermal energy. In terms of the work-energy theorem, the work done by friction, which is negative, is added to the initial kinetic energy to reduce it to zero. The work done by friction is negative, because is in the opposite direction of the motion (that is, , and so ). Thus . The equation simplifies to
or
This equation can now be solved for the distance .
Solution
Solving the previous equation for and substituting known values yields
Discussion
The most important point of this example is that the amount of nonconservative work equals the change in mechanical energy. For example, you must work harder to stop a truck, with its large mechanical energy, than to stop a mosquito.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?