| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Rockets range in size from fireworks so small that ordinary people use them to immense Saturn Vs that once propelled massive payloads toward the Moon. The propulsion of all rockets, jet engines, deflating balloons, and even squids and octopuses is explained by the same physical principle—Newton’s third law of motion. Matter is forcefully ejected from a system, producing an equal and opposite reaction on what remains. Another common example is the recoil of a gun. The gun exerts a force on a bullet to accelerate it and consequently experiences an equal and opposite force, causing the gun’s recoil or kick.
Hold a balloon and fill it with air. Then, let the balloon go. In which direction does the air come out of the balloon and in which direction does the balloon get propelled? If you fill the balloon with water and then let the balloon go, does the balloon’s direction change? Explain your answer.
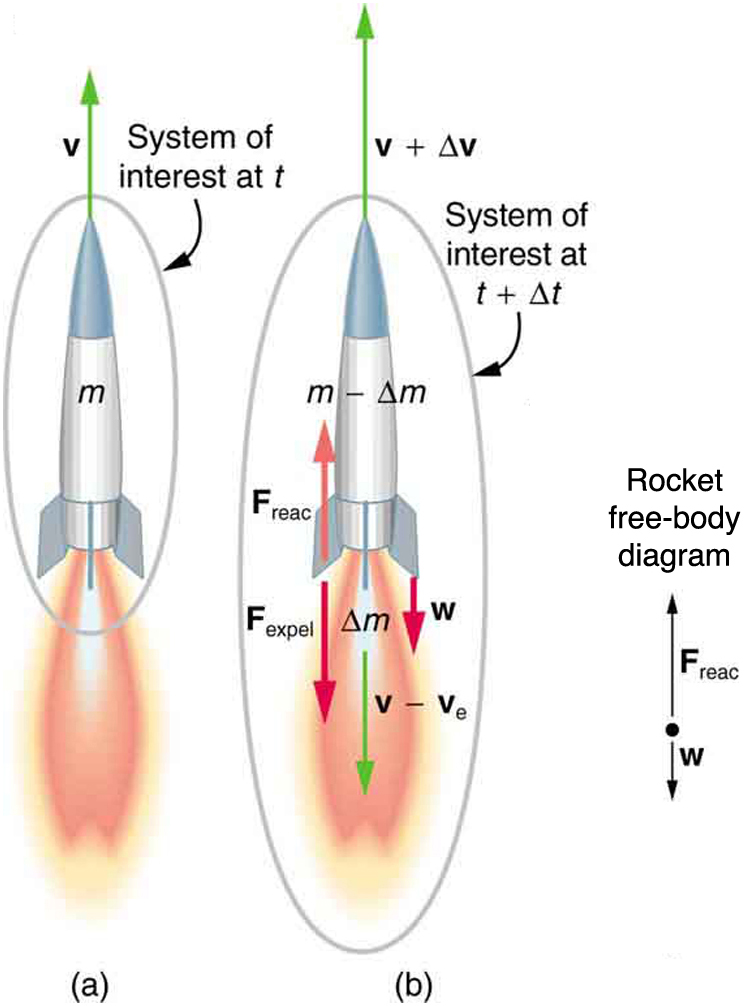
[link] shows a rocket accelerating straight up. In part (a), the rocket has a mass and a velocity relative to Earth, and hence a momentum . In part (b), a time has elapsed in which the rocket has ejected a mass of hot gas at a velocity relative to the rocket. The remainder of the mass now has a greater velocity . The momentum of the entire system (rocket plus expelled gas) has actually decreased because the force of gravity has acted for a time , producing a negative impulse . (Remember that impulse is the net external force on a system multiplied by the time it acts, and it equals the change in momentum of the system.) So, the center of mass of the system is in free fall but, by rapidly expelling mass, part of the system can accelerate upward. It is a commonly held misconception that the rocket exhaust pushes on the ground. If we consider thrust; that is, the force exerted on the rocket by the exhaust gases, then a rocket’s thrust is greater in outer space than in the atmosphere or on the launch pad. In fact, gases are easier to expel into a vacuum.
By calculating the change in momentum for the entire system over , and equating this change to the impulse, the following expression can be shown to be a good approximation for the acceleration of the rocket.
“The rocket” is that part of the system remaining after the gas is ejected, and is the acceleration due to gravity.
Acceleration of a rocket is
where is the acceleration of the rocket, is the escape velocity, is the mass of the rocket, is the mass of the ejected gas, and is the time in which the gas is ejected.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?