| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the previous two sections, we considered only one-dimensional collisions; during such collisions, the incoming and outgoing velocities are all along the same line. But what about collisions, such as those between billiard balls, in which objects scatter to the side? These are two-dimensional collisions, and we shall see that their study is an extension of the one-dimensional analysis already presented. The approach taken (similar to the approach in discussing two-dimensional kinematics and dynamics) is to choose a convenient coordinate system and resolve the motion into components along perpendicular axes. Resolving the motion yields a pair of one-dimensional problems to be solved simultaneously.
One complication arising in two-dimensional collisions is that the objects might rotate before or after their collision. For example, if two ice skaters hook arms as they pass by one another, they will spin in circles. We will not consider such rotation until later, and so for now we arrange things so that no rotation is possible. To avoid rotation, we consider only the scattering of point masses —that is, structureless particles that cannot rotate or spin.
We start by assuming that , so that momentum is conserved. The simplest collision is one in which one of the particles is initially at rest. (See [link] .) The best choice for a coordinate system is one with an axis parallel to the velocity of the incoming particle, as shown in [link] . Because momentum is conserved, the components of momentum along the - and -axes will also be conserved, but with the chosen coordinate system, is initially zero and is the momentum of the incoming particle. Both facts simplify the analysis. (Even with the simplifying assumptions of point masses, one particle initially at rest, and a convenient coordinate system, we still gain new insights into nature from the analysis of two-dimensional collisions.)
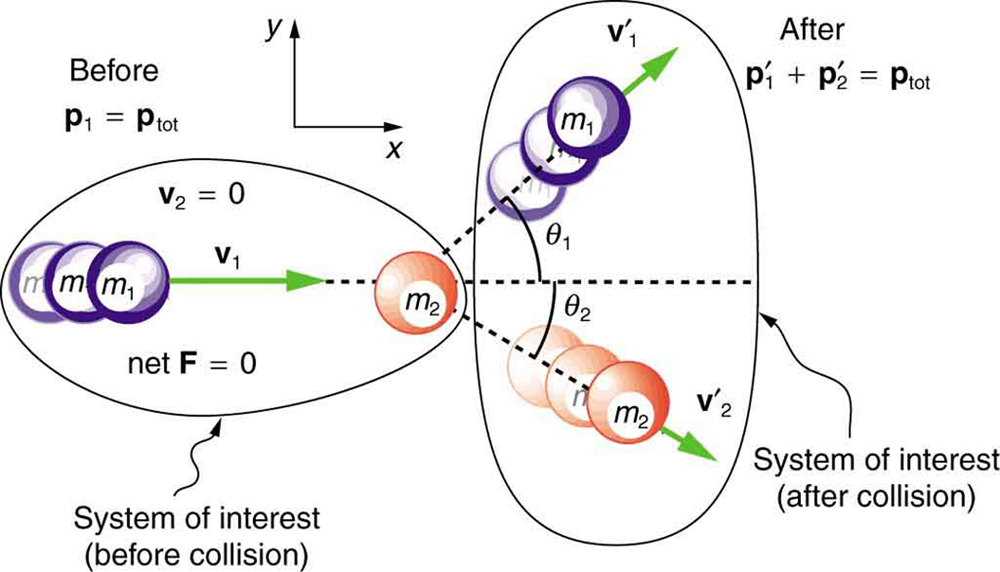
Along the -axis, the equation for conservation of momentum is
Where the subscripts denote the particles and axes and the primes denote the situation after the collision. In terms of masses and velocities, this equation is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?