| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We now move from consideration of forces that affect the motion of an object (such as friction and drag) to those that affect an object’s shape. If a bulldozer pushes a car into a wall, the car will not move but it will noticeably change shape. A change in shape due to the application of a force is a deformation . Even very small forces are known to cause some deformation. For small deformations, two important characteristics are observed. First, the object returns to its original shape when the force is removed—that is, the deformation is elastic for small deformations. Second, the size of the deformation is proportional to the force—that is, for small deformations, Hooke’s law is obeyed. In equation form, Hooke’s law is given by
where is the amount of deformation (the change in length, for example) produced by the force , and is a proportionality constant that depends on the shape and composition of the object and the direction of the force. Note that this force is a function of the deformation —it is not constant as a kinetic friction force is. Rearranging this to
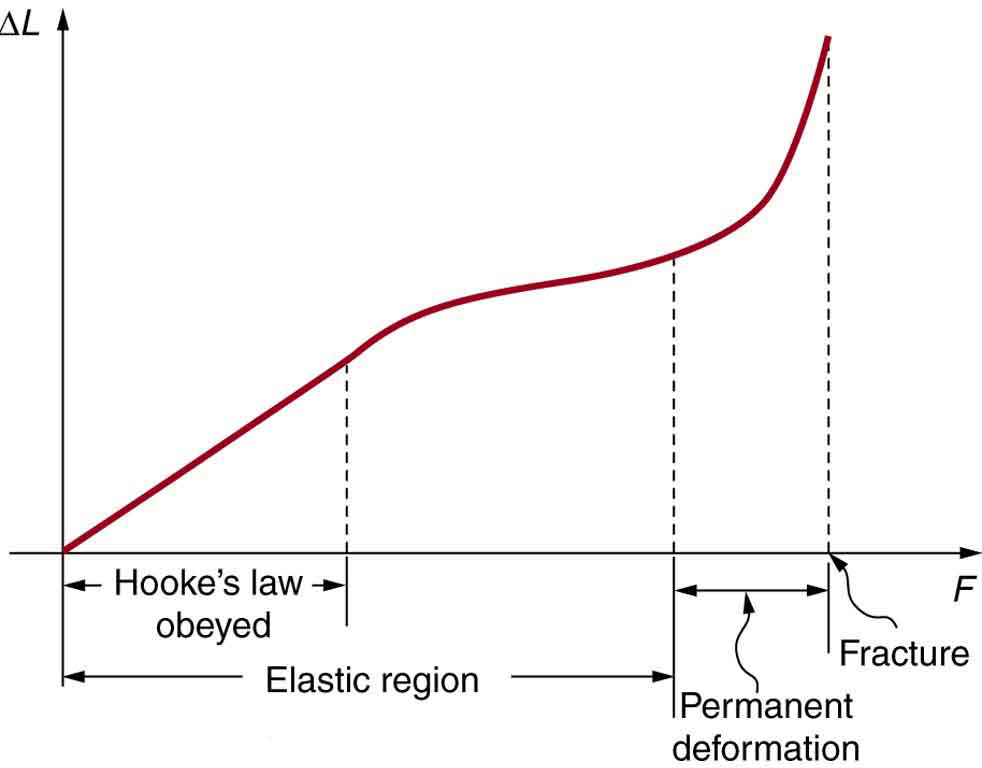
makes it clear that the deformation is proportional to the applied force. [link] shows the Hooke’s law relationship between the extension of a spring or of a human bone. For metals or springs, the straight line region in which Hooke’s law pertains is much larger. Bones are brittle and the elastic region is small and the fracture abrupt. Eventually a large enough stress to the material will cause it to break or fracture. Tensile strength is the breaking stress that will cause permanent deformation or fracture of a material.
where is the amount of deformation (the change in length, for example) produced by the force , and is a proportionality constant that depends on the shape and composition of the object and the direction of the force.
The proportionality constant depends upon a number of factors for the material. For example, a guitar string made of nylon stretches when it is tightened, and the elongation is proportional to the force applied (at least for small deformations). Thicker nylon strings and ones made of steel stretch less for the same applied force, implying they have a larger (see [link] ). Finally, all three strings return to their normal lengths when the force is removed, provided the deformation is small. Most materials will behave in this manner if the deformation is less than about 0.1% or about 1 part in .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'College physics' conversation and receive update notifications?